10 Real Estate Software Development Companies in 2025
- February 03
- 9 min

An IoT integration platform is a centralized system that connects, manages, and analyzes data from various IoT devices and sensors, enabling communication and coordination across a network. It acts as the backbone for automating processes, optimizing operations, and delivering actionable insights in real-time for enhanced efficiency and decision-making.
When applied to property management, IoT serves as a great tool to streamline operations and optimize resources. For large-scale property portfolios, where managing dozens or even hundreds of buildings can be a logistical challenge, IoT offers a way to centralize and automate critical tasks.
As IoT technology becomes more accessible, the challenge isn’t deciding whether to implement it, but how to do so effectively for complex, large-scale property portfolios. This guide aims to provide a clear, actionable roadmap for property managers, IT teams, and decision-makers who want to develop and deploy an IoT integration platform that maximizes the value of their diverse portfolios.
Key aspects covered in this guide include defining the requirements of your property portfolio, designing a scalable and interoperable IoT platform, and overcoming common challenges such as cybersecurity risks and scalability concerns. Examples, strategies, and best practices will also be shared to help you approach IoT integration with confidence.
This guide is tailored specifically for large-scale portfolios, whether they consist of residential, commercial, or mixed-use properties. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to plan, implement, and optimize an IoT integration platform that enhances every aspect of property management.
Key takeaways:
Developing an IoT integration platform for large-scale property portfolios requires careful planning and understanding of the requirements specific to the properties and stakeholders involved. This process involves assessing the types of properties managed, identifying key challenges, pinpointing IoT use cases, and involving critical stakeholders. Below, we’ll break down these essential considerations.
Large-scale property portfolios often comprise diverse property types, each with unique demands. Understanding these is the first step in building a tailored IoT integration platform.
Types of Properties
Portfolios typically include one or a combination of the following property types:
Managing large-scale property portfolios can be complex, with common challenges including:
Understanding these challenges provides clarity on how IoT systems can be used to improve operations and tenant satisfaction.
Once the portfolio needs are assessed, the next phase is identifying the specific IoT applications that will address those needs. Here are some of the most impactful use cases for property management.
IoT-enabled energy management systems leverage smart sensors and devices to monitor and control utilities like lighting, HVAC systems, and appliances. By analyzing energy patterns, these systems recommend adjustments to achieve savings and meet sustainability goals. Smart meters, for instance, can track usage in real time, allowing property managers to better allocate resources.
IoT devices can reduce unplanned downtime by continuously monitoring equipment, such as elevators, HVAC units, and other critical systems. Sensors collect data on performance and detect anomalies, alerting managers to address potential issues before breakdowns occur. This minimizes disruptions and reduces repair costs.
IoT technologies strengthen security through features like biometric access, surveillance cameras with AI-powered analytics, and smart locks. With centralized management, property managers can grant or revoke access and monitor activity across an entire portfolio remotely in real time, enhancing both safety and convenience.
Improved tenant satisfaction is a direct result of IoT integration. Devices like smart thermostats, customizable lighting systems, and mobile app-based controls offer personalized experiences. Tenants can easily manage their dwelling environment while enjoying conveniences like automated maintenance requests, leading to better retention and occupancy rates.
By focusing on these use cases, property managers ensure that IoT technologies deliver measurable value across the portfolio.
Stakeholder collaboration is crucial to the success of an IoT integration platform. Each group involved has a unique role to play, contributing to smoother implementation and more effective outcomes.
|
Stakeholder |
Role/Responsibilities |
|
Property Managers |
Primary users of IoT platforms who oversee multiple sites. They depend on the system to streamline operations, monitor properties, and make decisions based on data insights. Their feedback on current processes and challenges is vital for platform design. |
|
Tenants |
End users of IoT-enabled devices, such as smart home systems and mobile app platforms. They provide feedback to refine features, ensuring usability and enhanced satisfaction. |
|
IT Teams |
Responsible for ensuring the technical feasibility of the platform. Their duties include system integration, network infrastructure management, cybersecurity, and ongoing maintenance. |
|
Third-Party Vendors |
Suppliers of IoT devices and software, delivering the components needed for the platform. They ensure device interoperability, product quality, and offer support services critical to platform performance. |
The collaboration of these stakeholders ensures that the IoT integration platform is aligned with the diverse needs of the portfolio.
Understanding the requirements of property portfolios forms the foundation for a robust IoT integration strategy. By assessing portfolio needs, identifying actionable use cases, and engaging stakeholders, property managers can create a platform that serves operations while delivering long-term value.
Setting up a well-oiled IoT integration platform requires thoughtful planning and strategic design to ensure robustness, scalability, and value creation. The essential facets of designing the IoT integration platform focus on core features, the underlying technology stack, and robust data management strategies.
Successful IoT integration relies on embedding fundamental features that address the complexities of managing large-scale property portfolios. Here are three indispensable components every IoT platform must have:
A centralized dashboard acts as the command center for the entire IoT ecosystem. From this interface, property managers can view, monitor, and control operations across all devices and properties in real-time. The dashboard simplifies oversight by displaying data from multiple buildings in a clear and concise manner, ensuring quick, actionable decision-making. For example, managers can instantly monitor energy usage, security notifications, and maintenance alerts for all locations from one interface.
The scalability of your IoT platform determines its ability to grow alongside your portfolio. Large-scale property management involves hundreds, sometimes thousands, of devices spread across different locations. The platform must be able to accommodate new properties and devices without an overhaul. Scalability ensures that as your property portfolio expands or tenant demands evolve, the IoT system can scale operations while maintaining stability and performance.
For IoT platforms, one of the most critical features is the ability to gather and process data in real time. Sensors and devices continuously generate information on energy usage, occupancy trends, equipment performance, and more. Real-time analytics convert this raw data into actionable insights, enabling property managers to make informed decisions quickly. For example, energy consumption trends can reveal opportunities for cost savings, or predictive maintenance data can help avoid equipment failures before they occur.
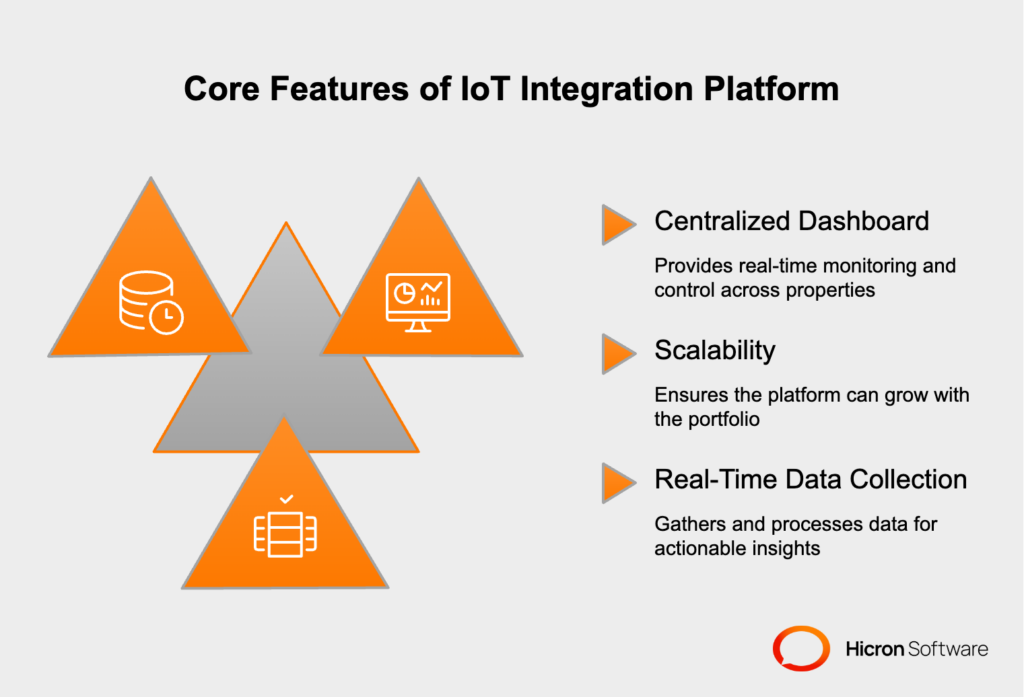
Combined, these features ensure the platform provides maximum value by streamlining operations, enhancing tenant satisfaction, and reducing operational costs.
Designing an IoT platform involves choosing the right technologies to form an interconnected ecosystem. The technology stack defines how your devices communicate, process, and store data while ensuring reliability and security.
The first layer of the stack includes various IoT-enabled devices and sensors capturing data on critical property operations. These might include:
These devices form the backbone of the IoT framework, collecting real-time data on critical building elements.
Communication protocols ensure uninterrupted interactions between IoT devices and the integration platform. Popular choices include:
|
Protocol |
Key Features |
Description/Use Case |
|
MQTT |
|
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol optimized for low-power, low-bandwidth IoT devices. Widely used in IoT platforms, it enables instant updates and reliable data transfer between distributed devices (like sensors, occupancy detectors, and maintenance monitors) and cloud services. Its scalability and efficiency make it ideal for industrial IoT, smart buildings, and remote monitoring, but extra security settings may be needed for sensitive deployments. |
|
Zigbee |
|
Zigbee is designed for reliable, low-data-rate device communication in confined or single-building environments. Its mesh topology allows devices to pass messages to one another, extending range and reliability even if individual devices lose connectivity. It’s commonly chosen for home automation, smart lighting, appliance control, and healthcare devices where low energy usage and secure short-range connectivity are priorities. |
|
LoRaWAN |
|
LoRaWAN is built for connecting devices spread across vast or outdoor areas, making it ideal for smart cities, agriculture, remote monitoring, and large property portfolios. Its strength lies in transmitting small packets of data over long distances with minimal power, such as for parking sensors, asset tracking, or environmental monitoring. Its lower data rate means it isn’t suitable for high-bandwidth needs like video streaming, but it excels at periodic, low-data tasks. |
Using the right communication protocol is crucial for balancing speed, range, and power consumption across devices.
IoT platforms require a robust infrastructure to store, process, and manage data. Decision-makers usually weigh two options:
Most large property portfolios benefit from a hybrid model, combining cloud flexibility with localized on-premises solutions for sensitive data.
With IoT devices generating massive volumes of data, managing this information effectively is essential. A well-structured approach ensures compliance with legal frameworks.
Data Collection, Storage, and Processing
IoT systems depend on vast amounts of data collected from sensors and devices across the portfolio. This data must be processed and stored to drive operational insights. Modern IoT platforms often utilize cloud databases for scalability combined with AI-backed engines to process data streams in real time, identifying patterns or anomalies for decision-making.
For example, an IoT-powered HVAC system may collect temperature and air quality data to adjust cooling or heating automatically, reducing waste and improving tenant comfort.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy Compliance
Managing large-scale portfolios means handling sensitive information from tenant activity patterns to access logs. To avoid risks, robust security measures must be integrated, such as:
Compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is one more layer. IoT platforms must offer functionalities to anonymize, regulate, and secure personal data to align with these legal requirements.
Designing an IoT integration platform requires a careful balance of powerful features, reliable technology, and robust data management practices. A centralized dashboard, scalable architecture, and real-time analytics ensure operational efficiency, while the selection of proper devices, communication standards, and infrastructure forms the foundation of a reliable IoT ecosystem. Strict adherence to data security and compliance standards guarantees the platform operates responsibly while safeguarding users’ trust. When these components align, property managers can transform large-scale portfolios into efficient, intelligent, and future-proof assets.
The pre-implementation phase is a critical stage in the development of an IoT integration platform. It involves all the preparatory work required to set the foundation for a successful project. If not handled properly, this phase can affect the overall timeline, either by delaying the project or by causing issues during later stages. Here’s an overview of the pre-implementation phase and its potential impact:
|
Activity |
Description |
Potential Impact of Neglect |
|
Stakeholder Alignment (2–4 weeks) |
Identify key stakeholders and agree on goals, scope, success metrics, and roles. Establish governance and decision cadence. |
Scope creep, conflicting priorities, rework, delays in approvals, and reduced adoption. |
|
Infrastructure Assessment (4–6 weeks) |
Audit networks, connectivity, power, devices, BMS/IT systems, and site readiness. Document gaps and dependencies. |
Integration failures, unexpected costs, bandwidth/latency bottlenecks, and deployment delays. |
|
Vendor and Technology Selection (4–8 weeks) |
Evaluate devices, protocols, platforms, and integrations for compatibility, scalability, and support. |
Vendor lock-in, poor performance, costly redesigns, and limited interoperability. |
|
Regulatory and Compliance Review (2–4 weeks) |
Map data privacy, security, and retention requirements; define controls and documentation. |
Legal exposure, failed audits, rework to meet standards, and launch delays. |
|
Budgeting and Resource Allocation (2–4 weeks) |
Build a detailed budget; assign internal/external resources, timelines, and KPIs. |
Funding gaps, resource conflicts, missed deadlines, and reduced project scope/quality. |
|
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Planning (2–3 weeks) |
Identify technical, security, operational, and vendor risks; define mitigations and contingencies. |
Unplanned outages, security incidents, cost overruns, and timeline slippage. |
Weeks indicate typical duration ranges based on portfolio complexity. Actual timelines may vary.
The pre-implementation phase typically takes 3-6 months, depending on the complexity of the project and the thoroughness of the planning. If this phase is rushed or poorly executed, it can add 2-4 months of delays to the overall timeline due to rework, misaligned goals, or unforeseen challenges.
By investing time and effort in the pre-implementation phase, you can avoid costly delays and set the stage for a smoother, more efficient development process.
Efficient monitoring and continuous optimization are pivotal to deriving maximum value from an IoT integration platform. The essential elements required to ensure IoT integration platform deliver ongoing performance improvements, user satisfaction, and operational excellence.
Tracking the right performance metrics offers valuable insights into the effectiveness of the IoT integration platform. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) allows property managers to assess progress and identify areas for improvement.
|
Metric |
Description |
Key Benefits/Examples |
|
Energy Savings |
IoT integration enhances energy efficiency by monitoring metrics like energy consumption per square foot, peak demand reduction, and overall utility cost savings. Automated systems such as HVAC scheduling and smart lighting optimize energy use efficiently. |
Achieving measurable impacts, such as a 20% reduction in energy costs through smart automation, directly contributes to sustainability goals and delivers tangible ROI for property managers. |
|
Downtime Reduction |
Reducing downtime ensures smooth operations and tenant satisfaction. By monitoring equipment uptime, maintenance alert frequency, and issue response times, IoT platforms facilitate predictive maintenance and prevent unexpected failures. |
For example, tracking a decrease in HVAC failures highlights how predictive maintenance minimizes disruptions, leading to lower operational costs and improved tenant trust. |
|
Tenant Satisfaction |
Enhancing tenant experience is central to IoT’s goals. Measuring tenant feedback scores, service request resolution times, and engagement with smart building features (e.g., app-based controls) ensures the platform meets user needs effectively. |
Increased tenant satisfaction promotes lease renewals, strengthens retention rates, and boosts the overall profitability of the property portfolio, ensuring long-term operational success. |
By continuously measuring these KPIs, property managers can make data-driven decisions to optimize both operational efficiency and tenant satisfaction.
Technology is constantly evolving, and a static IoT platform can quickly fall behind. Continuous improvement ensures your system remains effective and relevant by using the latest advancements and adapting to emerging needs.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning enable the IoT platform to analyze vast amounts of data and generate predictive insights. For example, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns in equipment performance, allowing the platform to predict potential failures or inefficiencies before they disrupt operations. Similarly, AI can optimize energy use in real time by adjusting systems based on occupancy trends, weather forecasts, or historical data.
These technologies not only improve performance but also create a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to property management, ensuring consistent tenant comfort and operational reliability.
Regular Updates and Feature Enhancements
IoT platforms must evolve to align with user needs and technological advances. Regular software updates ensure that your platform benefits from the latest features, improved security protocols, and better functionality. Over time, enhancements such as more intuitive dashboards, new analytic tools, or expanded device compatibility can boost usability.
Staying ahead of the curve with updates also extends the overall lifespan of your IoT platform, maximizing your initial investment while keeping your property portfolio competitive.
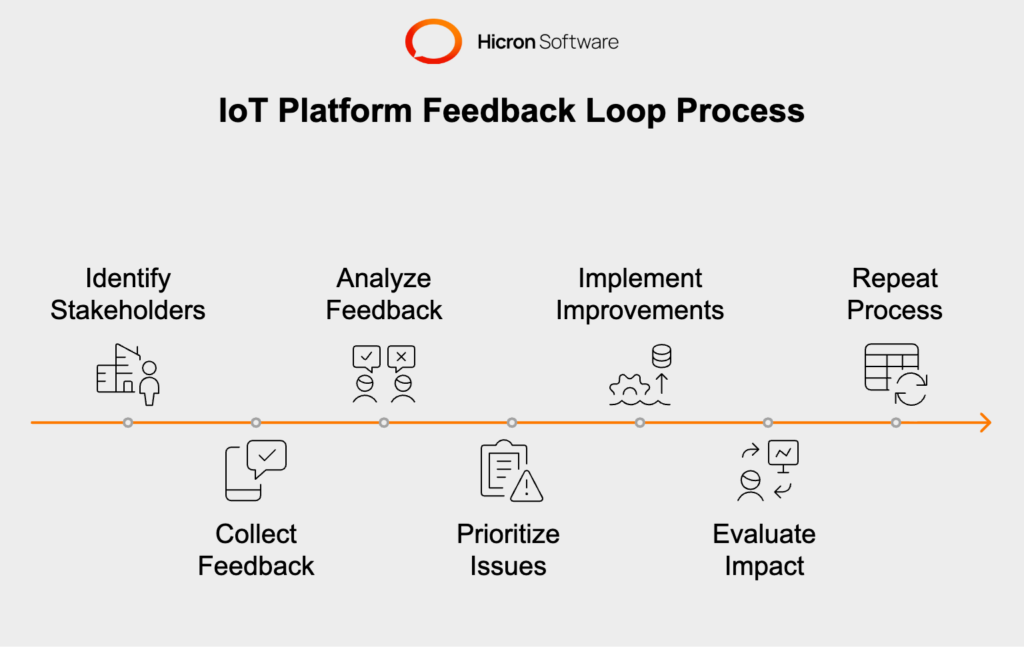
Refining your IoT platform is an ongoing process that requires input from those who use it daily. Establishing structured feedback loops ensures the system evolves in alignment with user experience and operational goals.
Collecting Input from Property Managers
Property managers interact with the IoT platform to monitor multiple buildings, manage devices, and evaluate data. By incorporating their feedback on system usability, functionality, and challenges, you can address pain points and refine features to enhance their workflows. Regular check-ins, surveys, and training sessions are effective ways to gather these insights.
Engaging Tenants
Tenants are another critical source of feedback, as they directly interact with smart technologies enabled by the platform. Their input on features such as smart lighting, app-based access control, or maintenance reporting can reveal opportunities for further optimization. Collecting this data through in-app feedback tools or tenant satisfaction surveys helps refine user-focused innovations.
Actionable Improvements
Equally important is how feedback is used. Prioritize common themes or recurring issues and implement changes that offer the greatest impact. For instance, if multiple property managers report difficulties with dashboard navigation, streamline the interface design, or provide additional customization. Addressing tenant concerns about connectivity issues might involve upgrading your infrastructure or switching to more reliable devices.
By maintaining active feedback loops, your IoT integration platform evolves into a system that aligns perfectly with its intended purpose, balancing innovation with everyday functionality.
Monitoring and optimizing your IoT integration platform is an ongoing endeavor that drives both immediate and long-term value. By focusing on meaningful performance metrics, leveraging modern technologies like AI, and fostering feedback loops with users, you ensure the platform meets its full potential. These efforts not only enhance operational efficiency and tenant satisfaction but also solidify the competitive edge of your property portfolio in an increasingly IoT-driven world.
In total, the initial development and deployment of an IoT integration platform can take 10-16 months, with ongoing improvements and scaling continuing indefinitely.
A successful IoT integration platform anticipates and mitigates common hurdles. Focus on scalable architecture, strong security controls, and disciplined financial planning to maintain performance and deliver long-term value.
|
Challenge |
Key Strategies |
Details/Examples |
|
Scalability |
|
|
|
Cybersecurity |
|
|
|
Cost Management |
|
|
By addressing scale, security, and cost early (and revisiting them as the portfolio grows) you keep the platform reliable, compliant, and financially defensible.
Building an IoT integration platform for large-scale property portfolios is a staged journey worth taking. Looking ahead, the most effective property platforms will blend AI-driven IoT with edge computing. Expect smarter anomaly detection, predictive maintenance that schedules itself, and automated energy optimization tuned to occupancy and weather. Edge processing will cut latency and bandwidth costs, unlocking faster control loops for critical systems. Open standards and digital twins will make cross-portfolio orchestration and simulation easier, while stronger cybersecurity and privacy controls become table stakes.
Start with a focused pilot, set measurable targets, and validate ROI within one or two buildings. Partner with experienced technology experts to de-risk architecture choices, accelerate integration, and establish a roadmap you can scale across your portfolio. With a clear plan and the right team, your platform can deliver measurable savings, resilient operations, and a better tenant experience, really fast.
An IoT integration platform is a centralized system that connects, manages, and analyzes data from IoT devices and sensors. It enables automation, real-time insights, and operational efficiency, making it essential for managing large-scale property portfolios effectively.
Common challenges include ensuring scalability to handle multiple properties and devices, maintaining robust cybersecurity to protect data and devices, and managing costs while achieving long-term ROI.
Key use cases include smart energy management, predictive maintenance, enhanced security and access control, and improving tenant experiences through personalized and automated solutions.
Property managers provide operational insights, tenants offer feedback on usability, IT teams ensure technical feasibility, and vendors supply interoperable devices and support services. Collaboration ensures the platform meets diverse needs.
Emerging trends include AI-driven IoT for predictive insights, edge computing for faster data processing, and digital twins for simulating and optimizing property operations. These advancements will further enhance efficiency and tenant satisfaction.
