InsurTech Innovations: Transforming the Insurance Industry
- November 14
- 8 min

Choosing the right core IT modernization strategy is crucial for insurance companies to secure scalability and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. A well-aligned approach ensures streamlined operations, future-ready systems, and the ability to stay ahead in the competitive insurance market.
Selecting the right approach to core IT modernization is a pivotal decision for any insurance company navigating its transformation journey. A well-chosen strategy serves as the foundation for efficient operations, scalable solutions, and lasting competitiveness in an industry increasingly shaped by technological innovation.
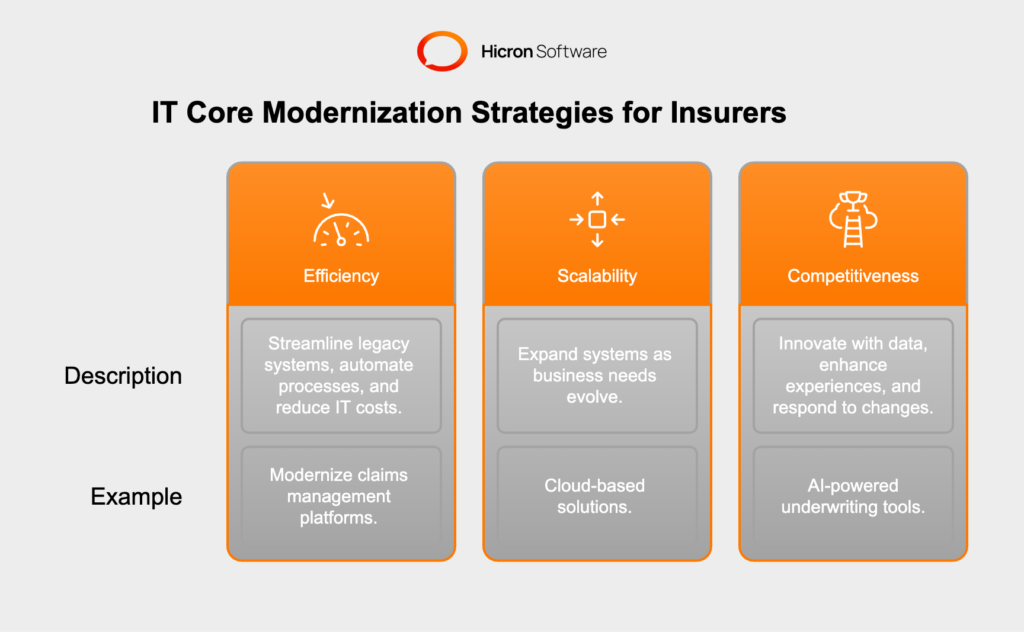
Efficiency lies at the heart of modern IT transformation in insurance. By adopting tailored core IT modernization strategies, insurers can streamline legacy systems, automate routine processes, and reduce IT maintenance costs.
For example, modernizing claims management platforms can reduce processing times and provide a seamless experience for policyholders, enhancing both productivity and customer satisfaction.
The insurance industry is no stranger to fluctuating demand, whether due to market trends, regulatory changes, or emerging risks. A strategically chosen modernization approach equips insurers with scalable systems that can expand seamlessly as business needs evolve.
Cloud-based solutions, for instance, enable companies to flexibly adjust IT resources, ensuring they can support growing customer bases and adapt to technological advancements without overhauling their infrastructure.
Competition in the insurance sector is fierce, and companies that fail to modernize risk falling behind. A robust IT transformation strategy empowers insurers to innovate with data-driven insights, enhance customer experiences through personalization, and respond swiftly to market changes.
Whether implementing AI-powered underwriting tools or leveraging advanced analytics for risk assessment, the right strategy sets the stage for long-term success.
Investing in a comprehensive, well-aligned core IT modernization strategy is not just a technological decision; it is a business imperative. For insurers embarking on their modernization journeys, the ability to balance efficiency, scalability, and competitiveness will define their trajectory in an increasingly digital landscape.
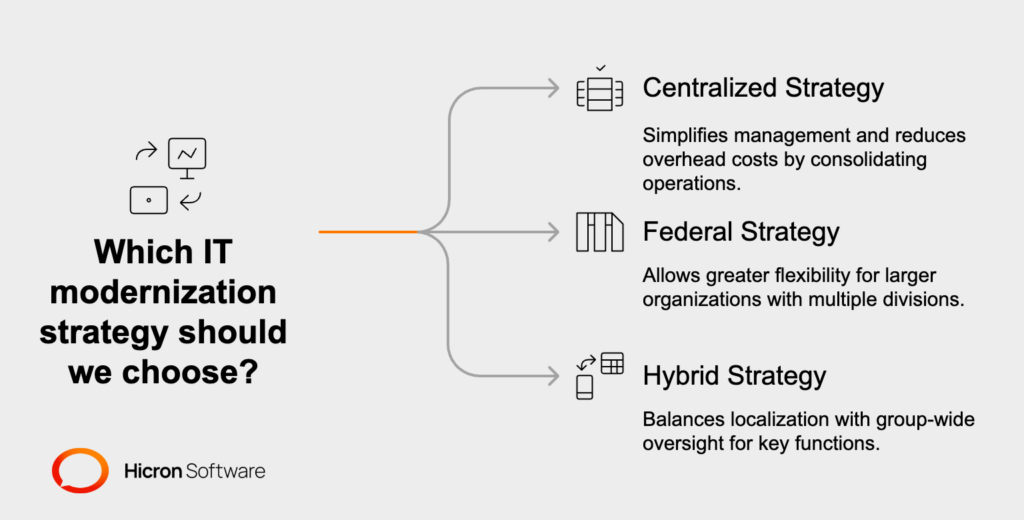
Selecting the right core IT modernization strategy is fundamental for insurance companies aiming to streamline operations and drive long-term growth. There are three primary approaches to consider: centralized, federal, and hybrid, each offering unique advantages depending on an insurer’s size, structure, and strategic objectives.
|
IT Modernization Strategy |
Description |
Ideal For |
Key Advantages |
Considerations |
|
Centralized |
Consolidates all IT functions under a single authority. |
Smaller organizations. |
|
Requires strong governance to align top-down decisions with operational needs. |
|
Federal |
Balances centralized oversight with decentralized execution, allowing autonomy for business units or regions. |
Medium to large insurers with diverse products or geographic footprints. |
|
May require careful coordination to maintain balance between autonomy and oversight. |
|
Hybrid |
Combines elements of centralized and federal models, offering flexibility to customize based on needs. |
Organizations undergoing IT transformation. |
|
Requires strategic planning to ensure the right balance of centralization and decentralization. |
Each of these strategies has specific strengths and trade-offs. By aligning the chosen approach to their unique size, structure, and goals, insurers can optimize resources and position themselves for growth in today’s digitized insurance landscape. Careful evaluation ensures that the core IT modernization strategy serves not only current business needs but also future innovation opportunities.
Adopting a centralized IT modernization strategy can be a game-changing approach for insurance companies seeking streamlined operations and consistent governance. This model consolidates all IT functions into a single, unified system, delivering multiple benefits tailored to organizations that prioritize uniformity and efficiency.
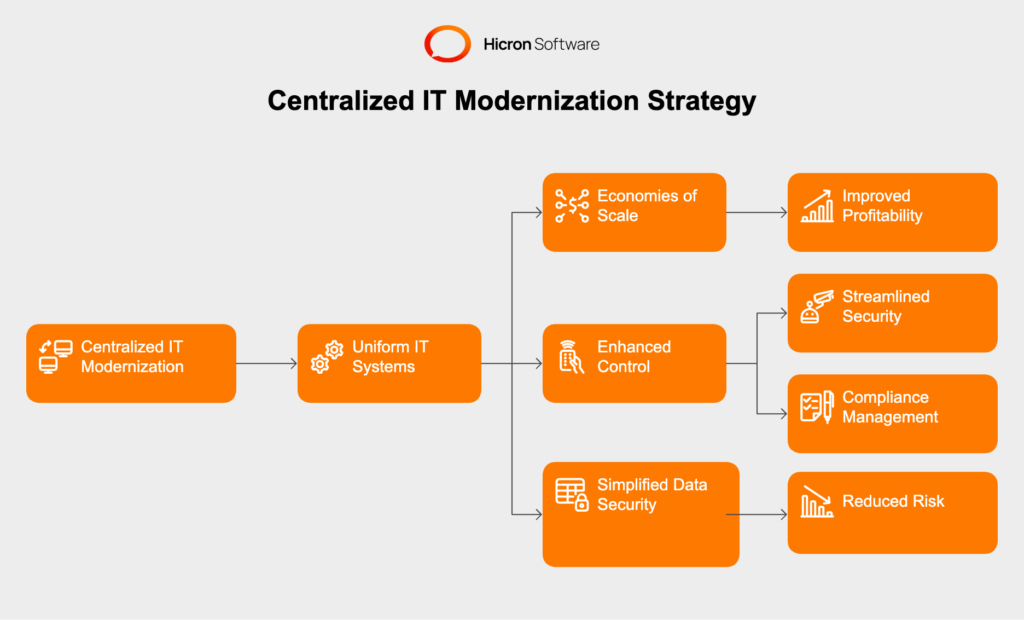
The primary benefit of centralized IT modernization is the creation of uniform IT systems, which improve operational consistency across the organization.
Standardization simplifies processes, reduces redundancies, and enables the straightforward implementation of company-wide policies. For example, a centralized claims processing system ensures that every branch follows the same protocols, minimizing errors and delays.
Consolidating IT systems under a central framework often reduces infrastructure and maintenance expenses. By managing resources centrally, insurers can benefit from economies of scale, such as bulk licensing agreements and unified vendor management, which directly impacts the bottom line.
Centralized strategies also enhance control and oversight. A single-point authority makes it easier to implement security measures and compliance protocols, critical for insurers navigating stringent regulatory environments. This centralized governance ensures data security and simplifies risk management on an enterprise level.
A centralized strategy works best for smaller insurance companies or those operating in highly regulated markets. Smaller firms often lack the complexity or geographic dispersion that necessitates more decentralized approaches, making centralized systems a practical choice. Similarly, insurers that offer a limited set of products benefit from the streamlined operations provided by this model, as their IT requirements are less varied.
Insurance organizations undergoing substantial digital transformation might use a centralized model as a foundation for modernization. By implementing centralized systems first, these companies can establish a strong, cohesive IT framework before expanding or diversifying their IT operations.
For insurers who value consistency, cost control, and streamlined governance, centralized IT modernization offers a proven path forward. By unifying systems under one roof, organizations can enhance efficiency and lay a stable groundwork for both current operations and future innovation.
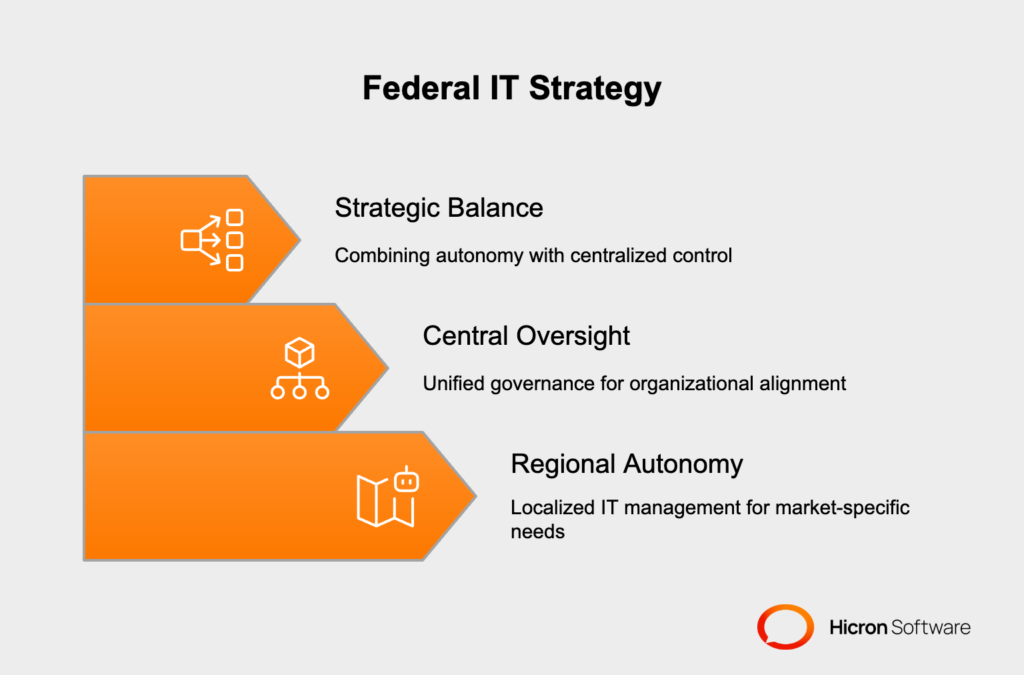
The federal IT strategy offers a balanced approach to modernization, combining regional autonomy with group-level oversight to meet the diverse needs of modern insurance organizations. This model is particularly well-suited for insurers operating across multiple regions, with varying customer demands and regulatory environments, as it ensures flexibility alongside unified governance.
At its core, the federal IT strategy revolves around empowering regional branches or business units to manage their IT systems independently while adhering to overarching guidelines and frameworks set by headquarters. This balance allows localized teams to
Meanwhile, central oversight ensures alignment with organizational goals, consistent security protocols, and streamlined resource allocation.
For instance, regional IT autonomy enables branches to adopt tools or systems tailored to their specific operational needs, such as localized underwriting applications. At the same time, group-wide policies ensure that these systems adhere to shared standards, ensuring data integration and consistency across the organization.
The federal IT strategy works best for medium to large insurance companies with geographically dispersed operations or diverse product portfolios. For instance:
By incorporating regional IT autonomy, insurers can innovate quickly and respond to dynamic market conditions, all while leveraging the stability that centralized oversight provides.
The federal core IT modernization strategy represents an ideal blend of flexibility and control. It empowers insurers to meet localized demands without sacrificing enterprise-wide consistency. By aligning regional autonomy with group-level governance, this approach enables organizations to drive innovation, reduce inefficiencies, and maintain robust insurance IT governance across their operations. For insurance companies navigating complex structures and markets, the federal strategy offers a path to scalable, sustainable modernization.
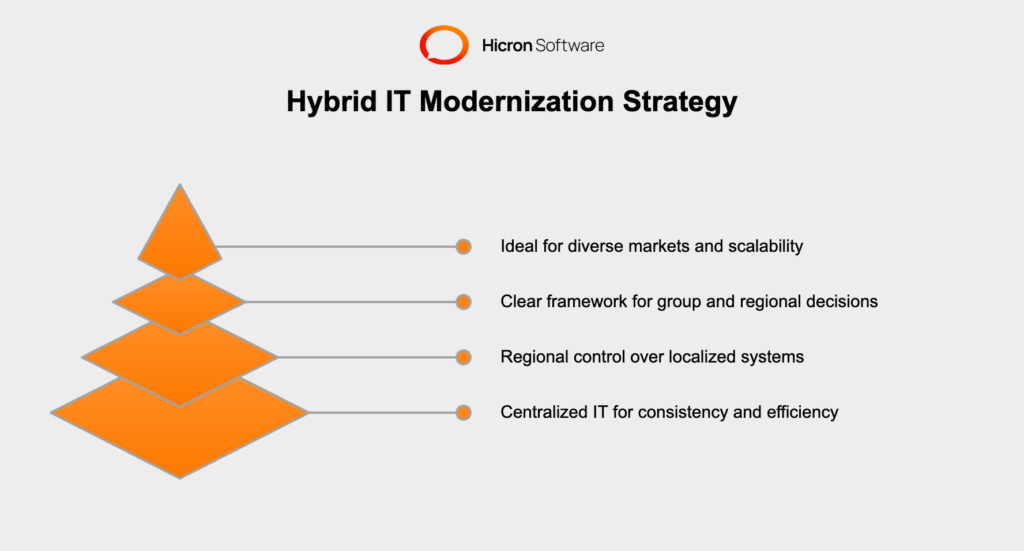
The hybrid IT strategy offers insurance companies an adaptable and balanced approach to modernization by combining elements of centralized and federal models. By leveraging the strengths of these two strategies, insurers can achieve a higher degree of flexibility while maintaining the infrastructure and governance needed for long-term success.
At its core, the hybrid modernization approach involves centralizing certain IT functions for consistency and efficiency while allowing regional or departmental teams the autonomy to manage localized systems and processes. This blend provides the best of both worlds: universal standards and flexibility to address specific operational needs.
For example, an insurer might centralize data storage and security protocols to ensure compliance and integration across the organization. Simultaneously, regional branches could retain control over customer-facing tools, such as mobile apps or policy management platforms, enabling them to cater to specific market conditions without compromising the overarching IT infrastructure.
A hybrid IT strategy thrives on a clear decision-making framework. Group-level leadership typically governs critical aspects like data protection, compliance, and overarching technology investments, ensuring a unified direction. Meanwhile, regional teams are empowered to make agile decisions tailored to their operational realities, enabling faster response times for market-specific shifts and customer demands.
For instance, in a hybrid strategy, the group-level team might standardize cloud systems across the company, while regional units select additional software tools to meet localized underwriting or claims processing requirements. This balance boosts efficiency and fosters innovation at the ground level.
The hybrid IT strategy is particularly advantageous for large insurance companies dealing with diverse markets or varied product portfolios. It also benefits insurers looking for scalability without compromising agility. Whether it’s a multinational insurer navigating global operations or a multi-line company managing different insurance products, the hybrid approach provides the flexibility and resilience needed to thrive in an evolving digital landscape.
The hybrid IT strategy empowers insurers to combine the strengths of centralization and regional autonomy in a way that supports both operational efficiency and market responsiveness. With this hybrid modernization approach, insurance companies can achieve insurance IT flexibility, addressing today’s demands while positioning themselves for future growth and innovation.
Achieving success in insurance core IT modernization requires a strategic approach grounded in proven principles. The following seven best practices provide a comprehensive roadmap for insurance companies to modernize their IT infrastructure effectively, regardless of their chosen strategy.
|
Step |
Description |
Benefits |
|
1. Align IT and Business Goals |
Align IT priorities with organizational goals like operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, or profitability to ensure modernization delivers tangible business value and supports long-term growth. |
|
|
2. Prioritize Customer-Centric Solutions |
Focus on building systems that improve customer experiences, such as streamlined claims processing or personalized policy management platforms, to strengthen competitiveness in the insurance market. |
|
|
3. Build a Scalable and Modular Tech Stack |
Design scalable, modular systems for easy updates and integration of new technologies, ensuring flexibility to adapt to market trends and regulatory changes while enabling cost-effective growth. |
|
|
4. Leverage Agile Methodologies |
Use agile methodologies to enable quicker, iterative transformations, allowing for efficient testing, refinement, and deployment of solutions while catching potential issues early. |
|
|
5. Ensure Robust Risk Management |
Develop risk management frameworks to identify and mitigate risks like operational disruptions or cybersecurity threats, and create contingency plans to ensure business continuity during challenges. |
|
|
6. Foster Collaboration Between Teams |
Promote collaboration between regional and group-level teams to align localized needs with group-wide objectives, maintaining consistency while addressing regional requirements. |
|
|
7. Measure Success Through Clear KPIs |
Define KPIs like system uptime, customer satisfaction, or time-to-market for new products to track modernization progress and ensure alignment with business goals. |
|
By following these IT modernization best practices, insurance companies can streamline the transformation process, minimize risks, and maximize outcomes. From strategic alignment to fostering collaboration, each of these principles contributes to building a robust, flexible, and future-ready IT infrastructure. With a well-executed core modernization effort, insurers can meet today’s demands while preparing for tomorrow’s opportunities.
Choosing the right IT modernization strategy is a critical step in any core technology modernization planning process. The decision should align with your organization’s unique requirements, ensuring that technological investments drive efficiency, scalability, and long-term success. To make the best choice, insurers need to consider key factors like company size and structure, the scope of operations, and available resources.
The size and complexity of your organization play a significant role in IT strategy selection.
If your company operates across multiple regions or international markets, this factor is crucial for determining the right modernization strategy.
Budget constraints and resource allocation also influence your decision.
When planning your IT transformation, weigh the long-term return on investment (ROI) against the short-term financial outlay to ensure the strategy aligns with both your immediate budget and future growth plans.
|
Step |
Description |
Key Considerations |
|
1. Assess Your Company’s Size and Structure |
Evaluate the size and complexity of your organization to determine the best IT strategy. |
|
|
2. Evaluate Regional vs. Global Operations |
Consider the geographic scope of your operations. |
|
|
3. Analyze Budget and Resource Availability |
Assess budget constraints and resource allocation. |
|
Selecting the best modernization strategy is a tailored process that requires careful consideration of your company’s objectives and capabilities. Whether you’re focusing on insurance modernization planning for a small, centralized business or navigating the complexities of a global insurer, aligning your choice with these critical factors ensures a successful and impactful IT strategy selection.
Choosing the right strategy for core IT modernization is essential for insurance companies navigating the complexities of today’s digital landscape. Centralized, federal, and hybrid strategies each offer distinct advantages, making them suitable for different types of insurers based on their unique needs and goals.
|
Strategy |
Description |
Ideal For |
|
Centralized |
Consolidates all IT functions under one authority to simplify management, reduce redundancies, and ensure consistency across operations. |
Smaller insurers or those with limited scale and straightforward operations. |
|
Federal |
Balances autonomy and oversight by allowing localized IT management while adhering to group-wide standards. |
Medium to large insurers with regional or global operations needing flexibility and alignment. |
|
Hybrid |
Combines centralized governance for critical functions with localized adaptability to meet specific requirements. |
Large, multi-faceted organizations undergoing complex IT transformations. |
Success in insurance IT transformation depends on selecting a strategy that aligns with your company’s broader goals. Whether prioritizing cost efficiency, operational flexibility, or scalability, ensuring that your modernization approach supports your organization’s current and future needs is key to achieving modernization strategy success.
The path to a successful IT modernization journey starts with a clear understanding of your organization’s vision and needs. By carefully evaluating which strategy best aligns with your objectives, you can position your company for long-term growth, innovation, and competitiveness in the evolving insurance industry. Take the first step today to design a modernization roadmap that secures your company’s future. Get in touch!
Core IT modernization involves updating and transforming an insurer’s IT systems to improve efficiency, scalability, and competitiveness. It ensures streamlined operations, future-ready systems, and the ability to adapt to a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Centralized Strategy: Consolidates all IT functions under one authority, ideal for smaller insurers seeking uniformity and cost efficiency.
Federal Strategy: Balances centralized oversight with regional autonomy, suitable for medium to large insurers with diverse operations.
Hybrid Strategy: Combines centralized and federal elements, offering flexibility and scalability for organizations undergoing IT transformation.
Insurers should consider factors like company size and structure, operational scope (regional vs. global), and budget. Smaller insurers may benefit from centralized strategies, while larger or geographically dispersed organizations might prefer federal or hybrid approaches.
Centralized strategies provide consistent standards, simplified management, cost efficiencies, and enhanced control over security and compliance. They are particularly effective for smaller insurers or those in highly regulated markets.
A hybrid strategy centralizes critical functions like data security and compliance while allowing regional teams to manage localized systems. This approach ensures operational efficiency and market responsiveness, making it ideal for large, diverse organizations.
Key practices include aligning IT with business goals, prioritizing customer-centric solutions, building scalable and modular tech stacks, leveraging agile methodologies, ensuring robust risk management, fostering collaboration between teams, and measuring success through clear KPIs.
