5 Strategies for Resilience & Growth in the Automotive Sector
- May 10
- 14 min

Scalable solutions for cross-platform fleet monitoring are flexible tracking systems designed to adapt and expand alongside your business operations. These solutions provide real-time vehicle tracking, predictive maintenance, and cross-platform integration capabilities that can be tailored to specific industry requirements and operational workflows.
This article explores how businesses can create fleet monitoring systems that scale effectively while integrating multiple platforms and data sources. You’ll learn the essential components for building adaptable fleet management systems and discover practical implementation strategies for different industries.
Key Takeaways:
Solutions for cross-platform fleet monitoring are software systems designed to unify data from a wide range of hardware, telematics devices, and software applications. They act as a central hub, collecting and standardizing information regardless of the original manufacturer or operating system. This unified approach provides a complete view of all assets on a single dashboard. As a result, businesses can scale their operations, adding new types of vehicles or equipment without being locked into a single technology provider.
Managing a fleet in today’s environment means dealing with a range of devices, operating systems, and business tools. Cross-platform solutions help your business bring these elements together, simplifying operations.
Cross-platform fleet monitoring solutions allow you to connect different types of hardware and operating systems under one system. This flexibility ensures that all vehicles and equipment, no matter their make or model, can communicate data effectively and be tracked in a single interface.
As software, devices, and regulations change, it is vital to maintain compliance and meet industry standards. Cross-platform solutions help your business stay current with the latest requirements, reducing the risk of penalties and making it easier to adapt to updates or new policies.
These solutions are designed to connect with your existing business software such as ERP, CRM, or accounting systems. This integration reduces manual data entry, supports automated workflows, and provides a more complete picture of your operations for better decision-making.
By consolidating data from every asset into one dashboard, you gain clearer insights into performance and costs. Access to unified fleet data helps identify trends, uncover inefficiencies, and supports better planning, ultimately leading to improved return on investment.
A truly scalable fleet monitoring system relies on core components designed for adaptability and efficiency. The core components include real-time GPS tracking with smart data processing, predictive maintenance through data analytics, compliance automation across multiple regions, and a multi-platform integration architecture. These foundational elements work together to create a platform that can grow with your operational demands.
|
Component |
Key Features |
Benefits & Applications |
|
Real-Time GPS Tracking |
|
Lower costs, faster notifications, reliable tracking |
|
Predictive Maintenance |
|
Less downtime, timely repairs, fewer false alarms |
|
Compliance Automation |
|
Easy cross-border compliance, reduced paperwork |
|
Multi-Platform Integration |
|
Unified data, improved accounting, better customer visibility |
Modern GPS tracking can process location data intelligently, filtering noise and providing actionable insights rather than overwhelming users with raw information.
Key features include:
The scalability comes from cloud-based processing that can handle data from 10 vehicles or 10,000 without performance degradation.
Predictive maintenance systems analyze multiple data streams to forecast equipment needs accurately.
combine to create maintenance schedules based on actual usage.
Fleet managers can configure alerts specific to their equipment types. Heavy construction machinery might monitor hydraulic pressure levels and engine temperature patterns.
Delivery trucks could track brake wear based on stop frequency and load weight patterns.
Machine learning algorithms improve prediction accuracy over time by analyzing maintenance outcomes against predicted schedules. This continuous learning process reduces false alerts and identifies previously unknown failure patterns.
Regulatory compliance becomes complex when fleets operate across different states or countries. Automated compliance systems apply appropriate regulations based on vehicle location and operational context. Custom solutions can automate compliance by:
For example, a logistics company operating across the US and Canada can have the system automatically switch between DOT and Transport Canada requirements as trucks cross borders.
Integration capabilities connect fleet monitoring systems with existing business software through APIs and data exchange protocols. This connectivity eliminates data silos and creates unified operational visibility.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP integration synchronizes fleet data with financial systems for accurate project costing and asset depreciation tracking. Work orders automatically update with vehicle assignments and completion status.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Platforms
CRM platforms receive real-time delivery updates that can be shared with customers through automated notification systems. Service response times feed into customer satisfaction metrics and billing calculations.
Maintenance Management Systems
Maintenance management systems receive predictive alerts and automatically schedule service appointments based on availability and priority levels. Parts inventory systems track component usage patterns to optimize stock levels.
Scalable fleet monitoring relies on modular architecture that allows independent component development and deployment. This approach enables businesses to start with essential features and add capabilities as operational needs evolve. Custom solutions use independent modules that can be added, modified, or scaled individually.
|
Layer |
Components |
|
Data Collection Layer |
|
|
Processing Layer |
|
|
Application Layer |
|
|
Data Storage Layer |
|
Data Collection Layer
The foundation includes telematics devices, mobile applications, environmental sensors, and third-party data feeds. Each component operates independently while contributing to the overall data ecosystem.
Telematics devices provide vehicle location, engine diagnostics, and driver behavior data. Mobile applications enable driver communication, inspection reporting, and job status updates. Environmental sensors monitor cargo conditions, fuel levels, and equipment performance.
Processing Layer
Real-time analytics engines process incoming data streams and generate alerts, reports, and automated responses. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and predict maintenance needs or operational inefficiencies.
Rule engines apply business logic and compliance requirements to raw data. Integration middleware manages data flow between fleet systems and external business applications.
Application Layer
User interfaces include web dashboards, mobile applications, reporting tools, and API endpoints for third-party integrations. Each interface can be customized for different user roles and operational requirements.
Fleet managers access comprehensive dashboards with real-time vehicle status, driver performance metrics, and maintenance schedules. Drivers use mobile applications for navigation, communication, and compliance reporting. Administrative users generate financial reports and compliance documentation.
Data Storage Layer
Specialized databases handle different data types and access patterns. Time-series databases store tracking and sensor data efficiently. Relational databases manage configuration settings and user information. Document storage systems handle compliance records and inspection reports.
Data warehouses aggregate information for long-term analysis and business intelligence reporting. Backup systems ensure data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
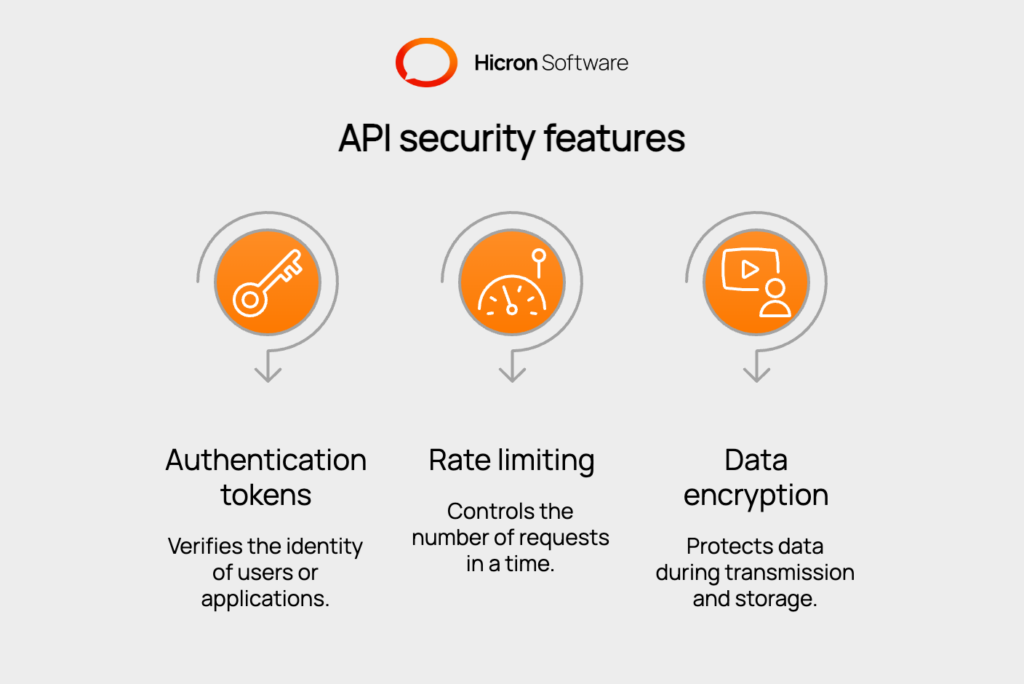
Custom fleet monitoring systems prioritize API development to ensure long-term flexibility and integration capabilities. Well-designed APIs enable easy connections with future business systems and third-party applications.
RESTful APIs provide standardized data access methods that work with most modern business applications. Webhook support enables real-time data sharing without constant polling. GraphQL endpoints allow applications to request specific data sets efficiently.
API versioning ensures backward compatibility when system updates introduce new features. Comprehensive documentation and developer resources facilitate third-party integrations and custom application development.
Security features include:
API monitoring tracks usage patterns and performance metrics to optimize system responsiveness.
Modern cloud platforms provide the foundation for truly scalable fleet monitoring systems. Auto-scaling capabilities automatically adjust computing resources based on demand and usage patterns.
During peak operational hours, the system allocates additional processing power to handle increased data loads. Off-peak periods trigger automatic scaling reductions to minimize operating costs.
Content delivery networks distribute data geographically to ensure fast response times regardless of user location. Edge computing capabilities process time-sensitive data locally to reduce latency for critical operations.
Redundancy across multiple data centers ensures continuous operation even during facility outages or maintenance periods. Automated backup systems protect against data loss while disaster recovery procedures minimize downtime during emergencies.
By integrating DevOps practices, organizations enable automated deployment and continuous management of their systems. This enhances the inherent scalability of cloud infrastructure, ensuring the fleet monitoring system operates at the optimal level.
|
Industry |
Key Features |
Benefits |
|
Logistics & Delivery (including E-commerce Fulfillment Centers) |
|
|
|
Construction Fleet Management |
|
|
|
Public Transportation Systems |
|
|
Successful implementation of custom fleet monitoring requires planning and a phased deployment.
Each implementation phase should include user training, system testing, and performance measurement to ensure successful adoption and maximum operational benefit.
Custom fleet monitoring systems require higher initial investment compared to standard software solutions.
Development costs include
Long-term benefits include
Most organizations experience a positive return on investment within 18 to 24 months through
Scalability advantages become more pronounced as fleets grow, since custom systems can accommodate expansion without requiring architectural changes or additional licensing fees per vehicle.
Technology evolution requires fleet monitoring systems to adapt continuously.
Begin implementation by conducting a thorough requirements analysis and identifying specific operational challenges that standard software cannot address effectively. Document current workflows and integration needs with existing business systems.
Select development partners with experience in both fleet operations and scalable system architecture. Ensure they understand your industry requirements and can provide ongoing support throughout system evolution.
Define success metrics and measurement criteria before implementation begins. Track key performance indicators such as fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, driver safety, and operational productivity to quantify system benefits.
Plan for gradual deployment starting with core features and adding capabilities over time. This approach minimizes operational disruption while allowing users to adapt to new systems incrementally.
Effective fleet monitoring solutions that work across different platforms often use cloud-based systems. These systems allow real-time tracking and data analysis, making it easy to manage fleets from anywhere. Devices like GPS trackers and sensors gather important information and send it to a central system for better oversight. Customizable software connections (APIs) help link fleet data with other tools businesses already use. Mobile apps make it simple for drivers and managers to stay updated and make decisions quickly. Smart tools powered by AI help predict maintenance needs and improve routes, ensuring these solutions are practical and easy to scale.
Custom solutions offer flexibility to match specific operational requirements, integration with existing business systems, scalability without performance degradation, and the ability to add features as business needs evolve. Standard software often requires businesses to adapt their processes to fit software limitations.
Development and deployment usually takes 4 to 8 months depending on complexity and integration requirements. This includes planning, development, testing, training, and gradual rollout phases. Modular approaches allow for phased implementation starting with core features.
Custom systems require regular updates, security patches, and feature enhancements. Cloud-based solutions handle most infrastructure maintenance automatically. Businesses typically need technical support for user training, system configuration, and integration with new business applications.
Custom systems implement enterprise-grade security including encrypted data transmission, secure authentication protocols, role-based access controls, and regular security audits. Cloud infrastructure providers offer compliance with industry standards such as SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
Yes, custom solutions are specifically designed for integration through APIs and data exchange protocols. They can connect with ERP systems, CRM platforms, maintenance management software, accounting systems, and other business applications to create unified operational visibility.
