QA – what is the work of a Quality Assurance Engineer? And how to become one?
- June 25
- 4 min
Software quality assurance is an integral part of the software development process. Businesses release new software periodically to meet customer expectations and stay alive in the competitive business world.
Key Takeaways on Software Quality Assurance (SQA)
While churning out software, they tend to use practices other than software quality assurance. It either leads to software failure in the production environment or increases development costs. Therefore, you must adhere to proper software quality assurance to prevent your business from getting into such a complex situation. This article is your ultimate guide to software quality assurance and how it benefits your business.
Software quality assurance refers to monitoring all software engineering processes, activities, and work items to ensure they comply with defined standards. Software quality assurance in software engineering works in parallel to software development, from defining software requirements to coding and release.
The fundamental principles of software quality assurance include:
Software QA brings many benefits to your organization. You enjoy higher customer satisfaction, reduced development costs, and less time spent on software development. Let’s discuss the advantages of software quality in detail:
Typically, it takes $50,000 to $1,000,000 to develop medium to large applications, and if you focus on something other than quality assurance, this cost can quickly increase. This puts your business under immense financial pressure.
SQA monitors your software development, and as soon as an issue arises, the quality assurance engineers tackle it immediately. That is why minor problems are resolved before becoming more complex and expensive.
Additionally, software with proper quality measures doesn’t need as much maintenance. This significantly reduces overhead costs, ensuring more efficient and cost-effective development.
Nothing can harm customer experience more than poorly functioning software. It leads to customers demanding refunds and leaving bad reviews that deter future opportunities. Fortunately, software quality assurance analyzes each aspect of the software development lifecycle.
If there are issues or the software lags, the quality assurance team will address them immediately, ensuring the final product functions smoothly and enhances the customer experience.
The business world is becoming highly competitive, and to stand out from the crowd, you must deliver quick software. You can still maintain quality even while being quick, and SQA ensures this balance.
The QA and development teams work together from the start, eliminating the need for rework. Hence, the development process is streamlined, resulting in less time to market.
Data breaches and cyber-attacks are common occurrences that can compromise customer privacy. However, SQA addresses this concern. The quality assurance team tests the software and identifies and fixes any weaknesses and vulnerabilities that may invite attacks. As a result, the software is robust and secure, safeguarding both the organization and its customers.
The software quality assurance standards include ISO 9000, Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), and Testing Maturity Model (TMM). Let’s discuss these in detail:
ISO 9000 is the most commonly used SQA standard. It involves a set of international standards defining the software quality management system requirements. The main goal of ISO is to improve your software product and service quality. It includes the following principles:
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a behavioral model that aids your organization in improving overall processes. It also plays a crucial role in productive and efficient behavior to minimize risks and defects in software development. Typically, CMMI comprises five stages, such as Managed, Defined, and Optimizing, and there are clear KPAs to achieve these maturity levels.
Another software quality assurance standard is the Testing Maturity Model (TMM), a framework that evaluates the maturity of software testing. This model aims to identify the maturity of your current software development efforts. You can then set targets to improve your software testing processes to achieve desired results.
Implementing software quality assurance in your organization isn’t a one-step process but encompasses various steps. For instance, you must define quality standards, plan SQA activities, and conduct regular reviews and testing.
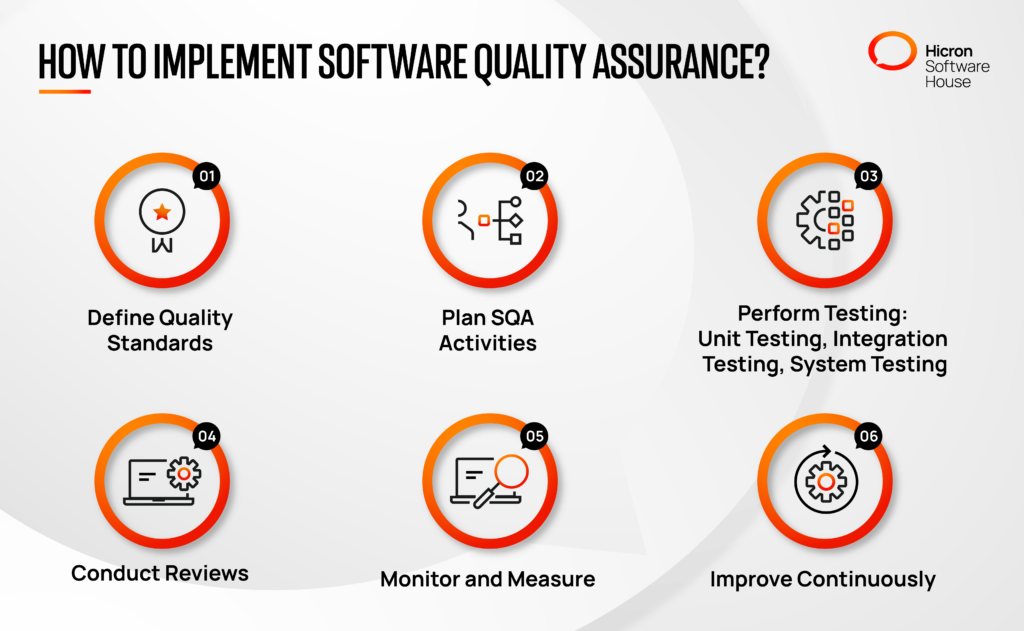
The first step in implementing quality assurance is clearly defining the software’s quality standards.
You should highlight the requirements and acceptance criteria for software. Additionally, you must outline key performance metrics that will help you measure the software’s quality.
Once you’ve done the planning, share it with all stakeholders, including development and testing teams. Make sure they understand everything, as it is pivotal for successful implementation.
Next, focus on planning the SQA activities. This includes scheduling regular reviews, testing, and software documentation throughout the development phase. During this stage, you should also assign roles so everyone is responsible and accountable for their specific tasks and everything is clear.
You must also employ a team other than the software development team to review different software aspects. For instance, they will review artifacts, design documents, and code to ensure you quickly identify defects and loopholes in the software early in the development process, which saves time and money.
You should also perform different types of testing for software process improvement. Some standard tests that you must include:
Once you’ve run all tests and deployed the software, you should constantly monitor its performance. For this, you can rely on critical metrics like code coverage and defect density. If you notice the software lagging or underperforming, quickly identify and address the root cause promptly.
Regardless of how efficient the software is, there will always be room for improvement. The final step is continuously enhancing your software quality by analyzing the collected metrics. For instance, if monitoring suggests the defect density has increased, you should implement rigorous testing from the start and validate the software functionality before deploying it.
The many tips to improve software quality include adopting automated testing, leveraging CI and CD, and cross-browser testing. Here is a detailed explanation of these points:
Most importantly, you must establish clear communication with all team members to improve the quality of the software. The software developers and quality assurance engineers should work collaboratively to verify that the software design meets quality requirements. There should be regular meetings and discussions with all stakeholders so everyone is on the same page work towards the same goals.
Implementing a robust software quality assurance plan from the beginning of your development process is crucial for ensuring your software meets the highest standards. By prioritizing SQA, you can avoid extensive rework, reduce costs, and deliver a superior product to your customers.
At Hicron Software, we deliver top-tier quality assurance testing services. Our expert developers conduct thorough performance and functional testing to ensure your software is free from bugs and defects. Partner with Hicron Software to ensure your software is reliable, secure, and ready to make a lasting impression. Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive QA testing and how we can help you achieve excellence in software development.
Software quality assurance refers to the systematic approach of overseeing all aspects of software development to ensure that the processes and final outputs align with pre-established quality benchmarks. It encompasses various activities, from initial planning to the final product release, to uphold consistency and reliability.
QA in software ensures that the development and functionalities of the software adhere to quality standards. By testing, verifying, and monitoring during different stages of the development lifecycle, QA detects issues and ensures that the product is reliable, efficient, and meets user needs before its release.
The role of software quality assurance (SQA) is to oversee the entire development process, ensuring adherence to standards, detecting potential problems early, and reducing the risk of defects. SQA provides a framework for quality management, improves development efficiency, and ensures a high-quality user experience by addressing issues before software deployment.
The four steps of quality assurance include planning, where quality goals and processes are defined; execution, which involves implementing the planned quality practices; assessment, where processes are monitored and standards are checked; and improvement, where feedback is used to refine future projects and enhance quality.
A QA engineer is responsible for designing, executing, and maintaining tests to ensure the software functions as intended. This includes testing for bugs, validating performance and usability, and collaborating with development teams to improve quality. QA engineers play a critical role in ensuring that software is efficient, reliable, and user-friendly.
The software assurance process involves a series of activities aimed at ensuring software safety, reliability, and security throughout its lifecycle. This process focuses on identifying risks, preventing defects, and ensuring adherence to industry standards, delivering a high-quality product that meets regulatory and user requirements.
QA roles do not always require coding, but it depends on the type of testing. Manual QA testing typically doesn’t involve coding, but automation testing often requires knowledge of programming languages like Java, Python, or JavaScript to create test scripts and work with automation tools.
The QA role includes ensuring the quality of software by planning and conducting tests, identifying and reporting issues, and working with development teams to resolve them. QA professionals verify that the software meets user requirements and performs efficiently and reliably before its release.
Some QA engineers write code, particularly those involved in automation testing. They design and execute automated test scripts to check software performance and functionality. However, coding is not always necessary for manual testers, as their role primarily involves executing pre-defined test cases.
Software quality assurance is crucial because it ensures that software meets the required standards for functionality, performance, and usability. It minimizes the risk of bugs, inefficiencies, and vulnerabilities that could negatively impact user experience or lead to financial losses. By focusing on defect prevention and adhering to industry or regulatory standards, SQA helps deliver reliable, high-performing software that satisfies both business objectives and customer expectations.
The principles of software quality assurance focus on delivering high-quality outcomes throughout the software development lifecycle. These include preventing defects early on, continuously improving processes, and following established standards to maintain consistency and reliability. SQA emphasizes collaboration among teams and prioritizes the needs of the end user, ensuring that the software is not only functional but also meets user expectations effectively.
Software quality assurance is a comprehensive process that oversees the entire development lifecycle to ensure overall quality, while software testing is a subset of SQA that focuses specifically on detecting and fixing defects. SQA is proactive, aiming to prevent problems through structured methodologies, whereas testing is reactive, concentrating on identifying existing issues. Essentially, SQA acts as the overarching framework, with testing playing a crucial role in achieving its goals.
Key tools in the SQA process include automation testing tools like Selenium and Appium, which simplify repetitive testing tasks. Additionally, systems for continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) enable teams to manage quality across iterative releases efficiently.
Automation enhances software quality assurance by making processes faster, more efficient, and consistent. Automated testing allows for continuous testing throughout development, ensuring issues are addressed promptly. It also scales effectively for large projects, reduces human error, and handles complex scenarios that are challenging to test manually. While there is an upfront investment in setting up automation, it delivers long-term cost efficiency, faster delivery times, and improved software quality, making it an integral part of modern SQA strategies.
SQA safeguards software by conducting in-depth vulnerability analyses and rigorous testing processes. By identifying weak points early and applying corrective measures, it significantly reduces the risk of breaches and ensures the software remains protected against potential cyber threats.
Core principles include defining clear quality goals, implementing structured assurance methods across development stages, tracking performance through software metrics, and fostering innovation by continuously refining processes based on outcomes and user feedback.
SQA enhances customer experience by delivering software that is dependable, easy to use, and aligned with user needs. Identifying problems before customers encounter them helps create a product that builds trust and positive engagement.
Yes, inadequate SQA can result in unchecked defects, poor user experience, security vulnerabilities, and increased costs post-launch.
Documentation facilitates clear communication, tracks quality benchmarks, and ensures consistency throughout the development lifecycle.
SQA identifies and resolves vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches, ensuring compliance with privacy standards and protections.
Rigorous testing and continuous monitoring help identify and fix defects, leading to lower crash rates
and improved reliability.
Success relies on clear quality standards, ongoing testing, high-quality data, collaboration, and adapting based on performance metrics.
SQA ensures software is tested for diverse conditions, enabling it to scale and perform efficiently across various environments.
SQA identifies potential defects, security vulnerabilities, and process gaps early in development, preventing costly errors later.
Implementing SQA reduces development costs, shortens the time to market, enhances customer satisfaction, and ensures software security by identifying issues early and addressing vulnerabilities.
SQA lowers costs by preventing expensive defects and minimizing maintenance needs. It accelerates timelines by streamlining processes and reducing rework through continuous quality checks.
Quality assurance is proactive and focuses on preventing defects during development, while quality control is reactive, verifying the final product meets specified requirements.
