POS ERP Integration: Benefits, Challenges and Best Practices
- November 12
- 20 min

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integral software solutions that centralize data and streamline core business functions like finance, HR, and supply chain. By unifying operations into a single system, ERPs enhance productivity, data accuracy, and decision-making, while also supporting scalability and regulatory compliance.
Integration of ERP with other business systems maximizes its potential. ERP system integration ensures consistent data flow across platforms, reduces manual data entry, and provides real-time insights. This leads to improved efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and scalable solutions that adapt to evolving business needs.
This blog aims to offer best practices for successful ERP integration. By following these guidelines, businesses can achieve seamless system connectivity, optimize workflows, and utilize integration tools effectively, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and data consistency.
ERP integration involves connecting an Enterprise Resource Planning system with other business systems and technologies to ensure seamless data flow and unified operations. This process enables various software applications to communicate and work together, consolidating information from different departments like finance, HR, inventory, and sales into a single, accessible platform. The scope of ERP integration can range from integrating simple data feeds to complex, bi-directional communication between multiple systems, ensuring that all business processes are synchronized and efficient.
Integrating ERP with other business systems offers numerous advantages that enhance overall business performance:
While the benefits of ERP integration are significant, organizations often face several challenges during the process:
By understanding these elements of ERP integration, businesses can better prepare for the integration process, mitigate potential challenges, and fully realize the benefits of a unified ERP system.
Before embarking on ERP integration, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of your current systems and processes. This involves:
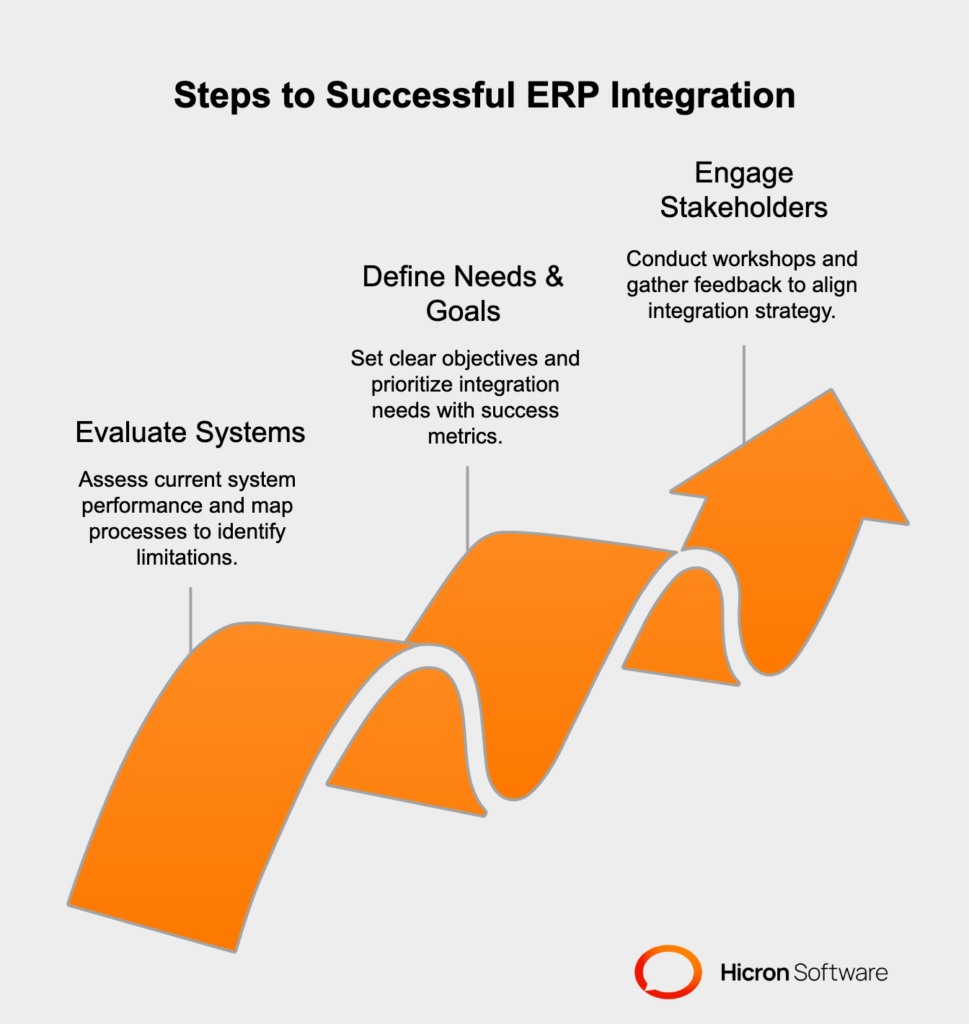
Once the current systems and processes are thoroughly assessed, the next step is to define the integration needs and goals. This includes:
Successful ERP system integration requires the involvement and buy-in of key stakeholders throughout the organization. To ensure all requirements and expectations are met:
By conducting a thorough assessment, identifying integration needs and goals, and engaging stakeholders, businesses can lay a solid foundation for a successful ERP integration that meets organizational objectives and enhances overall efficiency.
When integrating ERP systems with other business applications, two primary approaches are commonly used: point-to-point integration and middleware solutions.
Each integration method comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks:
|
ERP Integration Method |
Definition |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Point-to-Point Integration |
Direct connections are established between individual systems to transfer data. |
|
|
|
Middleware Solutions |
Middleware serves as an intermediary layer that facilitates communication between multiple systems, centralizing and simplifying integration logic. |
|
|
Choosing the right integration approach depends on several key factors:
|
Criteria |
Point-to-Point Integration |
Middleware Solutions |
|
Scale of Integration |
Suitable for smaller businesses with limited integration needs. |
Ideal for larger enterprises with complex and extensive integration requirements. |
|
Budget and Resources |
Budget-friendly upfront but may incur higher long-term maintenance costs due to limited scalability. |
Requires higher initial investment but offers significant long-term cost savings through easier management. |
|
Future Growth and Flexibility |
Limited flexibility to scale and adapt to additional integrations as business needs grow. |
Highly flexible and scalable, accommodating evolving business requirements and future integrations. |
|
Technical Expertise |
Minimal technical expertise required, making it easier for smaller teams to manage. |
Requires specialized knowledge for implementation but reduces the burden on individual system connections over time. |
By carefully assessing your business needs, integration scale, budget, future growth, and technical expertise, you can select the most appropriate integration approach to ensure a seamless and efficient ERP system integration.
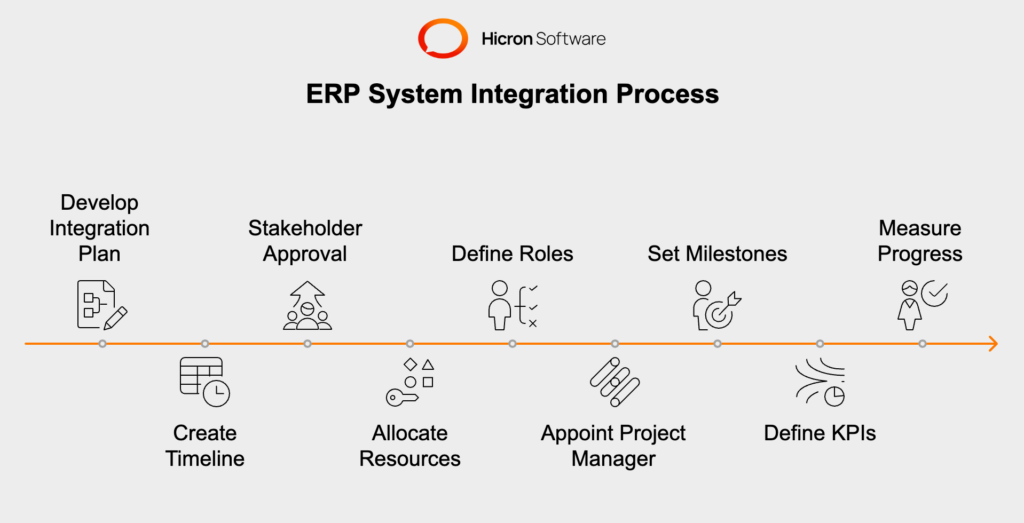
A successful ERP integration starts with a well-structured plan and timeline:
Effective resource allocation and clear role definitions are crucial for a successful integration:
To keep the integration on track and assess success, establish milestones and KPIs:
By developing a comprehensive integration plan and timeline, allocating resources effectively, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and setting realistic milestones and KPIs, businesses can ensure a structured and successful ERP integration process that meets their objectives and enhances operational efficiency.
Data consistency and standardization are critical for ERP integration. Consistent data ensures that information is uniform across all systems, facilitating accurate reporting and decision-making. Standardization helps in harmonizing data formats, units, and definitions, reducing the risk of errors and misinterpretations. By maintaining data consistency and standardization, businesses can ensure that integrated systems communicate effectively, supporting reliable and efficient operations.
Effective data mapping and transformation are essential to achieve compatibility between different systems. Key techniques include:
To sustain data quality and consistency, establish robust data governance policies:
By prioritizing data consistency and standardization, employing effective data mapping and transformation techniques, and establishing robust data governance policies, businesses can ensure high data quality and compatibility across integrated systems, leading to successful ERP integration and enhanced operational efficiency.
Integrating ERP systems with other business applications is a complex task that requires robust tools and middleware solutions to ensure smooth data flow.
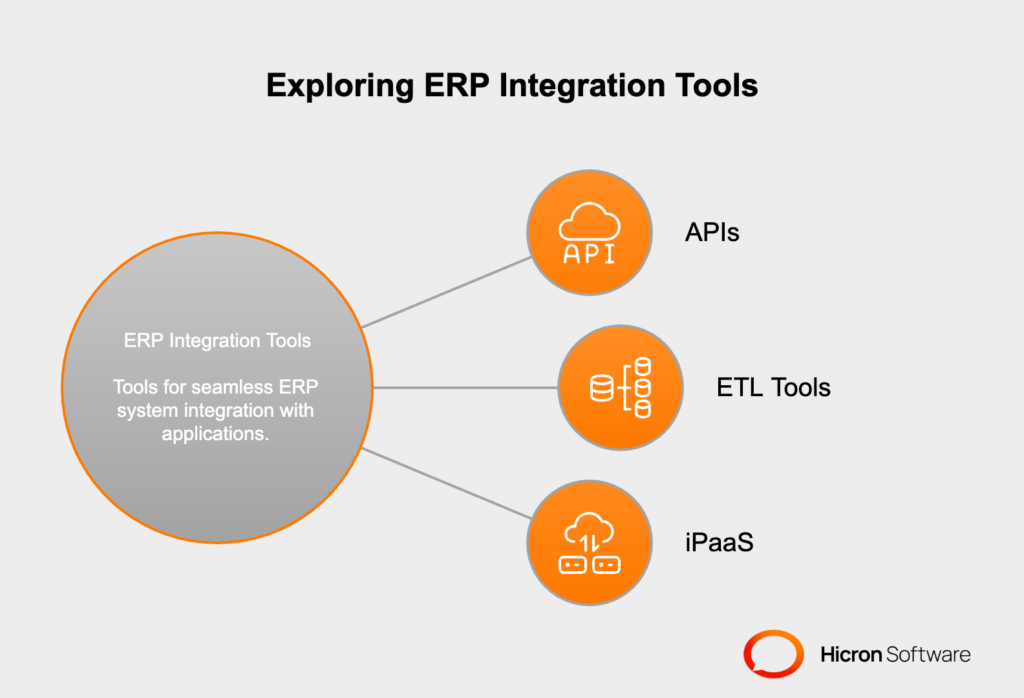
Here’s an overview of the most popular options:
Choosing the appropriate integration tools and technologies depends on several key factors:
|
Tool/Technique |
Description |
Example/Tip |
|
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) |
Serve as a bridge between your ERP system and other software, enabling real-time data exchange. |
Example: An API might connect your ERP to an inventory management system, ensuring stock levels are updated immediately after a transaction. |
|
Middleware Solutions |
Intermediary software that centralizes integration logic, helping manage, scale, and troubleshoot connections between multiple systems. |
Example: Middleware can sync data from a CRM, payroll software, and supplier database into your ERP without requiring individual connections between each system. |
|
ETL Tools (Extract, Transform, Load) |
Extracts data from various sources, transforms it into a compatible format, and loads it into the ERP, ensuring data consistency and accuracy. |
Example: An ETL tool can harmonize customer data from legacy systems and import it into a new ERP platform, avoiding manual entry and errors. |
|
Data Mapping |
Establishes relationships between data fields in your ERP and other systems for accurate data transfer. |
Tip: Use data mapping diagrams to visualize how information flows between systems, identifying gaps or redundancies. |
|
Data Transformation |
Converts data into a format compatible with the ERP system, essential for combining information from varied sources with different formats. |
Tip: Automate routine transformations using ETL tools to reduce manual intervention and errors. |
|
Real-Time Syncing vs. Batch Processing |
Real-time syncing updates data instantly, while batch processing handles large data chunks periodically based on system capabilities. |
Tip: Use real-time syncing for critical processes like inventory updates; batch processing is better for non-urgent data such as archived reports. |
|
Assess Compatibility |
Ensures integration tools work seamlessly with both ERP and other connected systems to prevent conflicts or data loss. |
Tip: Check compatibility before choosing tools to ensure smooth operation and avoid integration issues. |
|
Consider Scalability |
Choose tools that can grow with your business to accommodate new applications or increased data volumes. |
Tip: Opt for scalable solutions to future-proof your ERP integration efforts. |
|
Evaluate Vendor Support |
Select tools and vendors that provide robust technical support and detailed documentation for easier integration management. |
Tip: Strong vendor support simplifies troubleshooting and ensures reliable integration outcomes. |
To maximize the benefits of integration tools and technologies, follow these best practices:
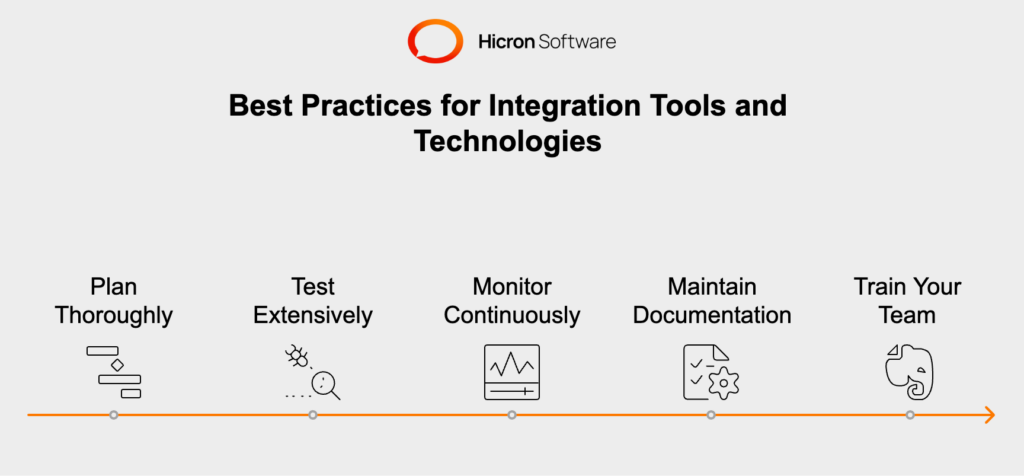
By leveraging the right integration tools and technologies, adhering to selection criteria, and following best practices, businesses can ensure successful ERP integration. This leads to improved efficiency, data consistency, and enhanced operational capabilities, ultimately supporting the organization’s growth and strategic goals.
Thorough testing before full implementation is essential to ensure the ERP integration functions correctly and meets business needs. It helps identify issues early, preventing disruptions and ensuring a smooth rollout.
By following these practices, businesses can ensure a reliable and efficient ERP integration, supporting their operational goals.
Successful adoption of a new integrated system starts with preparing your team. Begin by communicating the benefits and importance of the new system to all stakeholders. Clearly outline how the changes will improve workflows, enhance productivity, and support overall business goals. Engage team members early in the process to gather feedback and address concerns, fostering a sense of ownership and cooperation.
Conduct comprehensive training sessions tailored to different user roles. Ensure that each team member understands how to use the new system effectively for their specific tasks. Utilize a mix of training methods, including hands-on workshops, e-learning modules, and step-by-step guides, to accommodate various learning preferences.
Provide ongoing support to reinforce training and address any issues that arise. Establish a helpdesk or support team to assist users with questions and troubleshoot problems. Regularly update training materials to reflect system updates and enhancements, ensuring that the information remains relevant and useful.
Effective change management is crucial for minimizing disruptions and ensuring a smooth transition. Develop a detailed change management plan that includes a clear timeline, key milestones, and communication strategies. Keep all stakeholders informed about the progress and any upcoming changes, emphasizing the positive impact on their work and the organization.
Encourage a culture of adaptability. How? By recognizing and rewarding team members who embrace the new system and contribute to its successful implementation. Address resistance proactively by listening to concerns, providing additional support, and demonstrating the tangible benefits of the integrated system.
By preparing your team, providing thorough training and ongoing support, and managing change effectively, businesses can ensure a smooth adoption of the new integrated system. This approach not only minimizes disruptions but also enhances the overall efficiency and productivity of the organization.
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the integrated system operates smoothly and efficiently. Implement real-time monitoring tools that can track system performance and detect anomalies promptly. These tools should alert the IT team about potential issues, enabling them to address problems before they escalate. Regular checks help maintain system stability, improve response times, and ensure data integrity throughout the integration.
To keep the integrated system performing at its best, it’s important to regularly review and optimize integration processes. Conduct periodic audits to assess the effectiveness of the integration and identify areas for improvement. Analyze workflows to pinpoint bottlenecks and redundancies, then refine processes to enhance efficiency. This ongoing optimization helps adapt the integration to evolving business needs and technological advancements, ensuring sustained performance.
User feedback is invaluable for optimizing the integrated system. Gather insights from end-users through surveys, feedback forms, and regular meetings. Understand their experiences, challenges, and suggestions for improvement. Leverage this feedback to make targeted enhancements that align with user needs and preferences. By continuously improving the system based on user input, businesses can ensure higher satisfaction, better usability, and more effective utilization of the integrated solution. This proactive approach not only resolves issues swiftly but also drives ongoing improvements, supporting long-term operational success and growth.
In this blog post, we’ve explored the critical aspects of ERP integration, covering the leveraging of integration tools and technologies, the importance of thorough testing, and essential strategies for training and change management. We also delved into the necessity of continuous monitoring and optimization to ensure the integrated system remains efficient and effective.
A well-planned and executed ERP integration is vital for achieving seamless connectivity between systems, enhancing operational efficiency, and supporting overall business growth. By following best practices such as selecting the right integration tools, conducting comprehensive testing, preparing your team through training and change management, and continuously monitoring and optimizing your system, businesses can achieve a successful integration that meets their strategic goals.
We encourage you to adopt these practices to ensure a smooth ERP integration process. Share your thoughts or seek further assistance on ERP integration by reaching out to us. Your feedback is invaluable, and we’re here to help you navigate your integration journey.
To integrate an ERP system:
Assess your business needs and choose an ERP solution that aligns with them.
Establish a clear integration plan, outlining the systems and processes to be connected.
Use APIs or middleware to link the ERP with existing platforms like CRM, HR, or supply chain systems.
Test the integration thoroughly before going live to ensure data flows seamlessly.
An example of ERP integration is connecting an ERP to a CRM system. For instance, integrating Microsoft Dynamics 365 with Salesforce enables seamless data sharing, such as syncing customer orders, sales data, and account information between platforms.
To implement ERP:
Plan: Define objectives, select an ERP system, and assemble a project team.
Analyze: Assess current processes and identify gaps the ERP will address.
Develop: Configure the system to meet company-specific needs.
Test: Conduct thorough testing to ensure functionality and data accuracy.
Deploy: Train staff, migrate data, and roll out the ERP system.
Optimize: Monitor performance and make adjustments as needed.
The five key components of ERP are:
Financial Management
Human Resources Management
Supply Chain Management
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Inventory and Order Management
An API (Application Programming Interface) in ERP allows different systems to communicate and share data seamlessly. For example, an API can enable an ERP to pull real-time inventory updates from a warehouse management system.
A fully integrated ERP system connects all business processes, from finance to supply chain, into a single unified platform. This ensures real-time data flow and eliminates silos, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
ERP integration service refers to professional assistance in connecting an ERP system with other software and tools. This service ensures seamless data exchange, process automation, and system compatibility.
ERP integration involves:
Using APIs or middleware for data exchange.
Mapping data fields between systems to ensure consistency.
Establishing workflows to automate processes.
Conducting end-to-end testing to confirm functionality.
ERP is enterprise software that manages core business processes, while SaaS (Software as a Service) refers to cloud-hosted software accessible via subscription. Some ERP solutions are available as SaaS, simplifying deployment and reducing infrastructure costs.
ERP in EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) refers to the integration that allows the ERP system to send and receive standardized documents (like purchase orders or invoices) electronically, improving efficiency and accuracy in transactions.
ERP integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution System) connects business planning processes with shop floor operations. For example, it enables real-time data sharing between production schedules in ERP and machine usage data in MES.
The three types of ERP data include:
Master Data (e.g., customer, product, supplier details)
Transaction Data (e.g., sales orders, invoices)
Metadata (e.g., configurations and system settings)
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is software that centralizes and streamlines company operations, such as finance, HR, and inventory management, into a unified system. It provides real-time visibility, enhances efficiency, and supports informed decision-making.
ERP integration is the process of connecting an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with other business software or tools to ensure seamless data flow and operational harmony. It consolidates information from different departments, such as finance, HR, and inventory, into one unified platform, enabling better collaboration and efficiency.
The benefits of ERP system integration include improved data accuracy, streamlined workflows, and enhanced decision-making. By eliminating manual data entry and synchronizing information across tools, integration boosts efficiency, reduces errors, and enables real-time insights into core business processes.
Common ERP integration methods include:
Point-to-Point Integration – Directly connects ERP systems to other software for simple requirements.
Middleware Solutions – Uses an intermediary platform to manage complex integrations, ideal for scalability.
API-Based Integration – Leverages APIs for real-time data exchange between ERP and other systems.
Determining ERP integration needs involves evaluating your current systems, identifying pain points, and setting clear business goals. This includes analyzing where processes are disjointed, understanding what functionalities need improvement, and defining measurable outcomes like reduced data errors or faster workflows.
The best tools for ERP connectivity are:
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) – For real-time communication between systems.
Middleware Platforms – Such as Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions for scalable, centralized integrations.
ETL Tools (Extract, Transform, Load) – For managing and transferring large amounts of data across systems efficiently.
These tools cater to different needs, helping ensure a smooth and effective ERP integration process.
