14 Different Types of Software Testing
- February 19
- 13 min
Node.js is a versatile, open-source tool that allows you to execute JavaScript on the server. Powered by Chrome’s V8 engine, it’s both swift and lightweight, making it an ideal choice for developing scalable applications.
Built on an event-driven architecture and a non-blocking I/O model, Node.js efficiently manages multiple requests simultaneously. Ryan Dahl introduced this technology in 2009 to tackle issues encountered with traditional web servers. Since then, it has gained widespread popularity among developers worldwide.
As of 2025, Node.js remains a robust choice for web development due to its regular updates and ability to adapt seamlessly to emerging trends.
Node.js employs a single-threaded, event-driven architecture that efficiently handles multiple connections simultaneously. Rather than creating a new thread for each incoming request, it utilizes an event loop that continuously monitors tasks and executes them asynchronously.
Upon receiving a request, Node.js delegates operations like file reading or database queries to the system. Once these operations are complete, callbacks within the event loop manage the outcomes without interrupting other processes. This approach facilitates asynchronous processing, making Node.js particularly well-suited for scalable applications such as real-time messaging platforms, APIs, and streaming services.
By integrating non-blocking I/O with event-driven programming, Node.js delivers swift performance while maintaining low resource consumption.
Node.js is a versatile tool for developing scalable web servers, crafting RESTful APIs, and creating real-time applications like chat platforms and online games. Its event-driven architecture efficiently manages numerous tasks simultaneously. Developers often choose Node.js for building microservices architectures, which promote modularity and ease of maintenance in software.
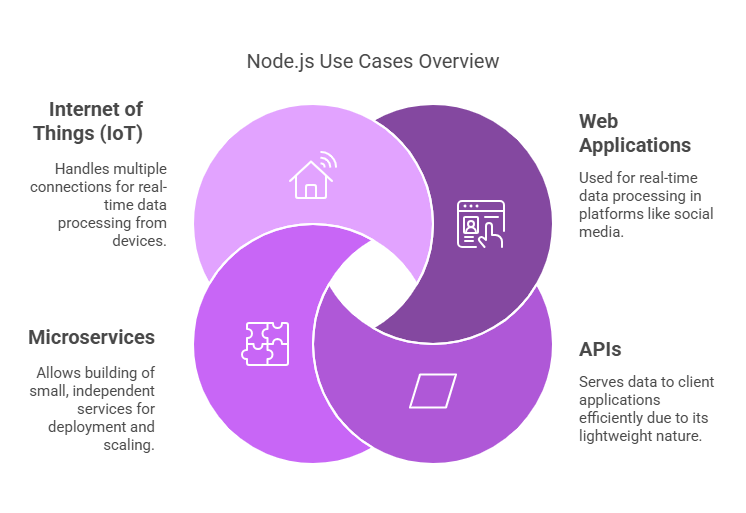
In the realm of streaming applications, Node.js excels by processing data in smaller chunks, making it suitable for video streaming services. Collaboration tools like Trello leverage its non-blocking I/O model to facilitate live updates among multiple users seamlessly.
Single-page applications (SPAs) benefit from Node.js’s ability to handle asynchronous requests, enhancing performance in dynamic web apps like Gmail or Facebook’s news feed. The Internet of Things (IoT) also benefits from Node.js due to its lightweight design and rapid execution speed, making it effective for managing connected devices.
Serverless computing platforms frequently incorporate Node.js for its quick startup times and minimal resource usage. It’s also widely used in DevOps automation scripts and command-line tools to streamline workflows.
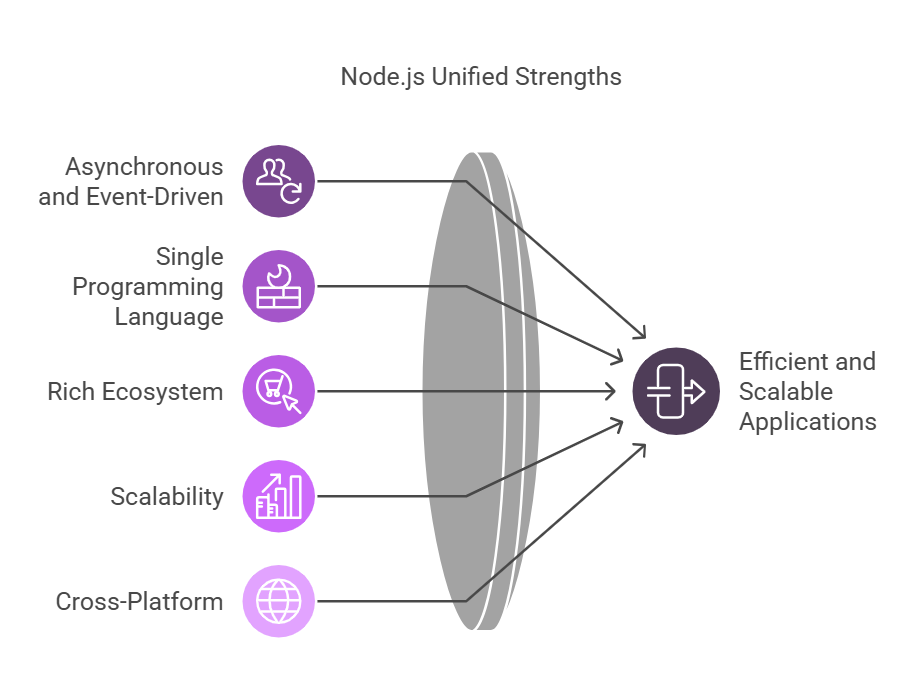
Node.js is a top choice for developing modern applications, thanks to several standout features:
Node.js offers plenty of advantages, but it also comes with certain challenges developers should consider:
To get Node.js up and running on your computer, follow these simple steps:
Node.js continues to be a favorite among developers in 2025, offering the tools needed to build high-performance applications. Its asynchronous, event-driven architecture is well-suited for projects of any size.
Node.js isn’t the best choice for tasks that require heavy CPU usage because of its single-threaded, event-driven nature. While it excels with tasks focused on input/output operations, it struggles when faced with demanding computations such as image processing or complex mathematical calculations. These types of tasks can block the event loop, leading to performance problems and delays in responding to other requests.
For handling CPU-intensive activities, developers often turn to worker threads available through Node.js’s `worker_threads` module. Alternatively, they might employ external services developed in languages like C++, Rust, or Python since these are more adept at parallel computing. Another strategy involves adopting a microservices architecture to distribute intensive operations across several services, which aids scalability.
Additionally, techniques like load balancing and utilizing message queues such as RabbitMQ or Kafka can help manage heavy workloads more efficiently while ensuring the main event loop remains responsive.
Google’s V8 engine is a high-performance JavaScript engine integral to Node.js, transforming JavaScript into native machine code for speedy execution. Though it was initially developed for Chrome, V8 significantly boosts Node.js by efficiently managing memory and enhancing performance through Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation.
This engine notably increases the speed and scalability of applications built on Node.js, making it especially suited for handling numerous connections simultaneously with minimal resources. Techniques like hidden class optimizations and inline caching further refine execution efficiency. Consequently, developers can craft lightweight and responsive applications that facilitate real-time interactions.
Continuously evolving with improved garbage collection and performance enhancements, V8 ensures that Node.js remains a favored choice in modern web development where rapid processing and efficiency are paramount.
In Node.js, the event loop is a crucial element that facilitates asynchronous programming. It handles multiple tasks simultaneously without interrupting the flow of execution. By continuously monitoring the event queue, it executes callbacks as soon as they become available. This non-blocking, event-driven model allows Node.js to manage numerous concurrent connections with ease.
When an asynchronous operation—such as file reading or database querying—is initiated, Node.js delegates it to the system and moves on to other requests. Once the operation completes, its callback is placed in the event queue and executed when there’s space in the call stack. This approach ensures smooth performance even under significant load.
The event loop consists of several stages:
These stages work harmoniously to optimize resource utilization and maintain application responsiveness—a feature particularly advantageous for real-time messaging services and APIs.
Thanks to this efficient use of resources through the event loop, Node.js can handle thousands of simultaneous connections while keeping resource consumption low. This makes it perfect for building scalable network applications.
Apart from Node.js, there are several other options such as Python, Ruby on Rails, Java with Spring, and Go.
Every alternative presents distinct advantages depending on what the application demands.
Node.js is gaining traction in innovative fields like AI, machine learning, and blockchain. As smart applications continue to evolve, developers are increasingly turning to Node.js along with AI tools such as TensorFlow.js and Brain.js to craft predictive models and automation systems. Thanks to its asynchronous design, it excels at processing data in real time, making it an excellent choice for developing chatbots and recommendation engines driven by artificial intelligence.
In the realm of blockchain development, Node.js plays a crucial role in crafting decentralized apps (DApps) and smart contracts. Its non-blocking I/O model ensures efficient management of numerous transactions across blockchain networks simultaneously. Tools like Web3.js facilitate straightforward interactions with Ethereum smart contracts, enabling secure peer-to-peer exchanges.
The scalability of Node.js makes it perfect for large-scale blockchain solutions that demand efficient transaction handling. By leveraging its lightweight execution model, businesses can create high-performance DApps while minimizing resource usage.
Ultimately, integrating Node.js with AI, machine learning, and blockchain broadens its functionality beyond traditional web applications. This expansion highlights Node.js as an essential component in emerging technologies that require speed, scalability, and real-time data processing capabilities. If you are looking for Node.js experts contact us.
