QA – what is the work of a Quality Assurance Engineer? And how to become one?
- June 25
- 4 min

Imagine your software or application failing right when users need it the most, leaving customers dissatisfied. It can become a reality if you don’t integrate proper testing into the software development lifecycle. There are many types of software testing, each designed to detect and eliminate different issues. Understanding the purpose and usage is essential for delivering high-quality products. To help you with this, we will discuss the different types of software testing with examples.
Software testing is a fundamental part of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It involves evaluating and verifying that a software application or system meets the specified requirements and functions correctly. This critical activity ensures the software is free from defects, performs as expected, and provides a high-quality user experience.
Software testing helps identify issues early in the development process through various testing methodologies, reducing the cost of fixes and enhancing overall product reliability.
Software testing has many benefits, including a low software failure rate, increased customer satisfaction, and potential money savings on coding rework. Let’s discuss these in detail:
High Security
The world is becoming increasingly digital, bringing many risks, including cyber security attacks. If your system or software isn’t secure, it can lead to data breaches and stolen customer information.
This damages your business reputation and makes you appear unreliable. However, software testing eliminates these worries.
The testing team runs tests to detect security vulnerabilities. In contrast, the development team applies multiple security layers to the software, making it secure and safe, which is critically needed by businesses like automotive, healthcare and banks.
Low Failure Rate
Another benefit of software testing is that it results in a low failure rate. How? It aids you in identifying your software’s capabilities and how much data or traffic it can handle. You can then optimize it so it doesn’t fail in the production environment.
For instance, suppose you’ve created an application that handles a specific load. You can run software stress testing to identify the breaking points and improve its performance under peak loads.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customers are your business’s most important asset, and you should always satisfy them. Software testing is a great help in this regard. It ensures the software is bug-free and works without lag across all devices and browsers. This makes customers happy and encourages them to become lifelong and loyal partners.
There are typically three different types of testing: automated testing, manual testing, and continuous testing.
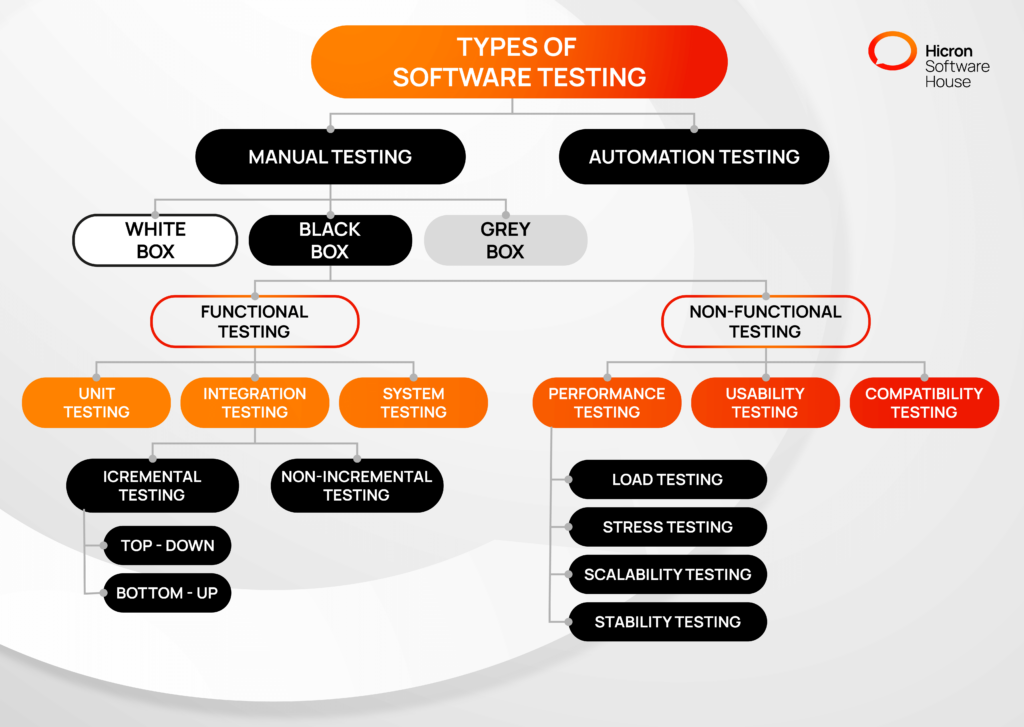
Here’s a detailed explanation of manual and automated testing to help you pick the right one:
Automated testing is a software test technique in which automation tools automatically test the software’s functionality. These tools help your business run multiple tests faster without any reliability issues.
The overview of the working of automation testing is given as:
The types of tests that are typically automated include API tests, unit tests, regression tests, and integration tests.
As the name implies, manual testing is the process by which software testers verify the quality of software manually. Test scripts are created by human labor, the testing environment is prepared, and tests are executed manually.
The following are some types of manual testing:
White Box Testing
Firstly, white-box testing, also known as transparent or clear-box testing, is a type of software QA testing. It’s performed by a QA professional or developer who understands how the internal code works. This manual testing type evaluates the internal structure and applications to find hidden errors, ensuring a smooth application flow.
Gray Box Testing
Then we have the Gray Box Testing is a mixture of both black and white box testing includes the tester receiving partial or improper information about the linking of applications. It mainly focuses on issues related to improper structure and improper use of applications.
Black Box Testing
Black-box testing is a critical manual testing method mainly based on the software’s functional aspect. Testers simply provide input and wait for output against the given information to check how well the software performs. It doesn’t require any knowledge of the internal technical systems and is best suited for finding discrepancies in the software application.
Manual testing is further divided into two main categories: functional and non-functional. Functional testing mainly checks whether the software’s outlined features are working as expected. Let’s discuss its many types:
Unit Testing
Unit Testing is an integral part of the software testing. In this, a small section or unit of the software is tested independently to verify if it’s working as per the design requirements. Here’s an example:
Scenario: Testing a “Password Strength Checker” feature for a website’s sign-up page.
Integration Testing
Another type of functional manual testing to test the application is integration testing. It involves running tests on the integrated or combined modules of the software to see if they are functioning properly when together. The main purpose of integration testing is to find inconsistencies and defects in the integrated units. The following example highlights this:
Scenario: Testing the integration of the “User Authentication” and “User Profile Management” modules in a web application.
System Testing
System testing is a high-level testing practice in which you run tests on both software and hardware. It enables you to check if the system complies with specific standards. Here’s an example that explains it in detail:
Scenario: Testing the entire restaurant booking system.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing is the last step in the testing process. It evaluates a system to ensure it meets all the requirements set by the business and users (User Acceptance Testing). The goal of running this test is to check if the software is ready for delivery.
Scenario: Acceptance testing for a new food delivery app.
Non-functional testing generally revolves around testing the various aspects of the software, like security and performance. It’s equally important as functional testing and has the following types:
Performance Testing
Software performance testing is actually a test of how fast and reliable a software system performs under different conditions. For instance, you can run it on different devices and browsers and check it working during peak load. If there are any lags or speed issues, you should immediately collaborate with the development team to fix them. The following example shows this:
Scenario: Checking the performance of a reading website under huge traffic.
It’s more mandatory than ever to make your software free of any vulnerabilities, and security testing helps you do that. It identifies loopholes and weak points in the application that hackers can make use of. You can then work with the software development team to enhance the security layers. Here’s an example:
Scenario: Security testing of a healthcare app.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a software testing type and is all about testing how intuitive your software application interface is for end users. It enables you to test different elements like navigation, control system, and overall visual design of the software that, if malfunctioning, can impact user experience.
Scenario: Usability testing of an e-commerce app.
There are some other types of software testing, such as Ad-Hoc Testing, Smoke Testing, Exploratory Testing, and Back-End Testing. Let’s discuss each one of them in detail:
It’s a pretty interesting type of testing, with no predefined plan or requirement. Instead, the tester clearly relies on their intuition to find any defects and vulnerabilities in the software.
It is random and unplanned and can be achieved via a technique called Error Guessing. It’s best when the testing team is running out of time to do elaborate testing but still wants to ensure the software is free of errors.
Back-end testing is also known as DataBase Testing. In this, the application’s server or database is tested to ensure it doesn’t have issues like deadlock, data loss, and data corruption. The database used in this type of testing can be anything like Structured Query Language (SQL) Server, MySQL, Sybase, DB2, or Oracle.
There are a few factors that you must consider when choosing the ideal testing approach for your business software project. For instance, you need to evaluate the time and budget you have for testing and testing objectives. An idea of the possible defects also makes the selection process easy.
First things first, you should consider the time and budget you can spare for testing. Typically, the software testing process takes anywhere from three to six weeks. So, you should check with your testing team and your resources to see if you can allocate that much time to testing. If yes, then you should adopt functional and non-functional testing methods.
Also, know that testing the software takes around 15% to 20% of your software development budget. If you are already low on budget, then you should use affordable testing like static testing.
Check what objective you want to achieve with testing. For instance, if you want to check the performance of your software under different conditions like load times or stress levels, you should focus on performance testing. However, suppose your goal is to make your application more user-friendly. In that case, it’s advisable to use usability testing to focus on how different software elements, like navigation and controls, contribute to a positive user experience. All in all, the objective you want to achieve also plays a crucial role in picking the right testing approach for your project.
Assess the complexity of your project to ensure the right testing is performed. For instance, for complex systems with multiple dependencies and integrations, you should go with integration testing. Besides, you should adopt penetration, compatibility testing, and security testing to ensure that the software product is robust and secure.
On the other hand, a simpler approach, like targeted unit testing, is sufficient for simpler software projects. You can test each section individually and tackle issues in small pieces, which is easier.
Many organizations don’t realize this, but software testing differs from software development. Therefore, you must train your team according to different testing requirements. For instance, if you want to conduct complex testing, ensure your employees receive regular training in advanced testing techniques and tools. This involves regular workshops, certifications, and courses that equip them with the skills to apply testing techniques efficiently and achieve the desired outcomes.
Also, make sure to pick testing methods that fit the developer’s perspective and cater to customer requirements. This ensures the software testing team is headed in the right direction and on track to provide an amazing customer experience.
Software QA testing is critical in ensuring the software application meets the highest quality standards and is ready to please customers. Are you wondering where to get excellent QA testing services for your software? The Hicron Software House is the ideal solution. We have a team of software testing and development experts who are well-versed in all types of testing. Whether it’s time for unit testing or performance testing, our team can handle everything to ensure your applications run flawlessly.
