Azure DevOps Guide
- April 25
- 62 min

Software migration is a process that involves transferring data, settings, and configuration information from an existing software application to a new one. Software migration, in essence, offers organizations a highly efficient way to remain competitive and relevant by upgrading to modern technology. Through proper software migration planning and execution, businesses can optimize their operations for the future.
The driving force behind software migration often lies in the limitations of outdated platforms. As hardware and operating systems evolve, old software may struggle to run smoothly or at all. To ensure seamless operations and optimized performance, organizations opt to migrate to newer software applications. A structured software migration plan helps organizations address these challenges efficiently.
Additionally, licensing plays a significant role in software migration. While vendors may offer licenses allowing organizations to use outdated technology without additional costs, those seeking access to new features and advancements may need to upgrade their software. This ensures the organization can leverage the full potential of the latest software versions through a robust software migration strategy.
By undertaking software migration, organizations can unlock a multitude of benefits, including enhanced productivity, improved security, and increased efficiency. Defining the software migration meaning for their needs, businesses can adopt new systems to adapt to evolving market demands, optimize workflows, and stay relevant.
When it comes to planning a software migration move, timing is an important factor to consider. The best time to move can vary depending on various factors such as conditions, personal circumstances, and availability of resources. A comprehensive software migration checklist can aid in identifying the right moment. Here are a few key considerations when deciding the ideal time for your move:
|
Outdated Technology |
Outdated technology can hinder your business’s potential by lacking essential modern features, security measures, or integration capabilities. Transitioning can enhance performance and support your evolving business needs with an effective technical migration plan. |
|
Vendor Dependency |
Dependency on vendors becomes problematic when they no longer support or provide limited assistance for old software solutions. By switching to alternative options with a well-defined software migration process, you can ensure ongoing maintenance, timely updates, and technical support. |
|
Business Growth and Expansion |
As your business grows, the limitations of your current software infrastructure may hamper its ability to handle increased demands. Migrating software allows you to scale your applications, process larger datasets, and expand into new markets. |
|
Cost Efficiency and Savings |
Optimizing cost efficiency and savings can be achieved by shifting to open-source alternatives or cloud-based solutions. This reduces licensing fees and maintenance expenses, optimizing your software spending and boosting financial results. |
|
Regulatory Compliance |
Regulatory compliance requirements, such as changing data privacy regulations or industry-specific standards, may necessitate a software migration. By adopting compliant solutions outlined in your software migration project plan, you ensure that your software meets legal and regulatory obligations. |
|
Data Center Consolidation or Cloud Adoption |
Migrating from on-premises data centers to cloud-based infrastructures offers benefits like increased flexibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure maintenance. Consolidating data centers or embracing cloud services aligns with effective software migration strategies. |
|
Integration and Interoperability |
Lack of integration capabilities and ineffective communication with other systems can hinder productivity. Migrating software to new solutions with improved integration streamlines workflows and enhances data exchange. |
|
Mergers and Acquisitions |
During mergers or acquisitions, organizations often need to consolidate operations and harmonize processes. Upgrading and migrating software systems facilitate proper integration, creating a unified and efficient business environment. |
A software migration project encompasses various intricate components, and the complexities of data management can pose challenges for organizations to varying degrees. Regardless of a business’s size or experience with change, meticulous software migration planning and strategic execution are critical for a successful transition.
To steer clear of common pitfalls that can derail software migration projects, here are five best practices to consider when your organization is gearing up for a software migration:
Proper software migration planning is the key to a seamless and efficient software migration process. Without a solid software migration plan in place, you run the risk of encountering delays, confusion, and increased expenses. It’s important to define your definition of success and establish performance benchmarks and KPIs for post-migration evaluation.You also should identify and address potential challenges and risks early on. By doing so, you will be better prepared to navigate obstacles and achieve your software migration goals.
Prepare for a successful software migration by gaining clarity on what needs to be moved, why, and the potential impact on your business. If you’re unsure where to begin, seek the expertise of an IT Consulting Firm. Take the time to identify and document the connections and inter-dependencies between your processes, systems, devices, and data. By doing so, you’ll be fully prepared and won’t overlook any crucial elements during the migration process.
To avoid unexpected setbacks and expensive errors, it is significant to have a clear understanding of the process and how each step contributes to the overall plan. It is important to establish what the process will involve and identify any connections between the steps. Additionally, it is necessary to determine the individual responsible for each step or activity. For instance, consider if a software migration architect is needed to lead the effort, and designate who will make the technical, design, and business decisions. It is also essential to identify who will oversee the post-migration environment. Lastly, outlining key milestones is important to ensure that each activity and person stays on track.
Involving representatives (from each department) in your software migration project can greatly contribute to its success. These representatives serve as a great role as the bridge between the software migration team and ground staff, ensuring effective communication and collaboration. Their involvement helps to share necessary information, address concerns, and maximize the chances of achieving the expected Return on Investment (RoI).
Performing testing before going live is essential, regardless of the constraints on your software migration timeline or the thoroughness of your planning process. Despite the potential time-consuming and cumbersome nature of checking every functionality or piece of data, skipping this step can lead to more serious issues down the line. Through rigorous testing, you can identify unexpected problems, address performance gaps, and ensure a smooth transition to the new environment.
A software migration plan is a structured approach to transitioning from one software system or platform to another while minimizing disruptions. It aims to ensure a smooth migration by addressing critical aspects like data transfer, system compatibility, testing, and user training.

Key components often include a thorough assessment of existing systems, a detailed timeline, risk mitigation strategies, and a rollback plan in case of issues. By carefully outlining every step, software migration planning helps organizations avoid downtime, protect data integrity, and ensure user adoption of the new system. This preparation is vital for maintaining business continuity throughout the transition.
Software migration process is the process of transferring a software application from one environment to another, such as upgrading to a new version or moving to a different platform.
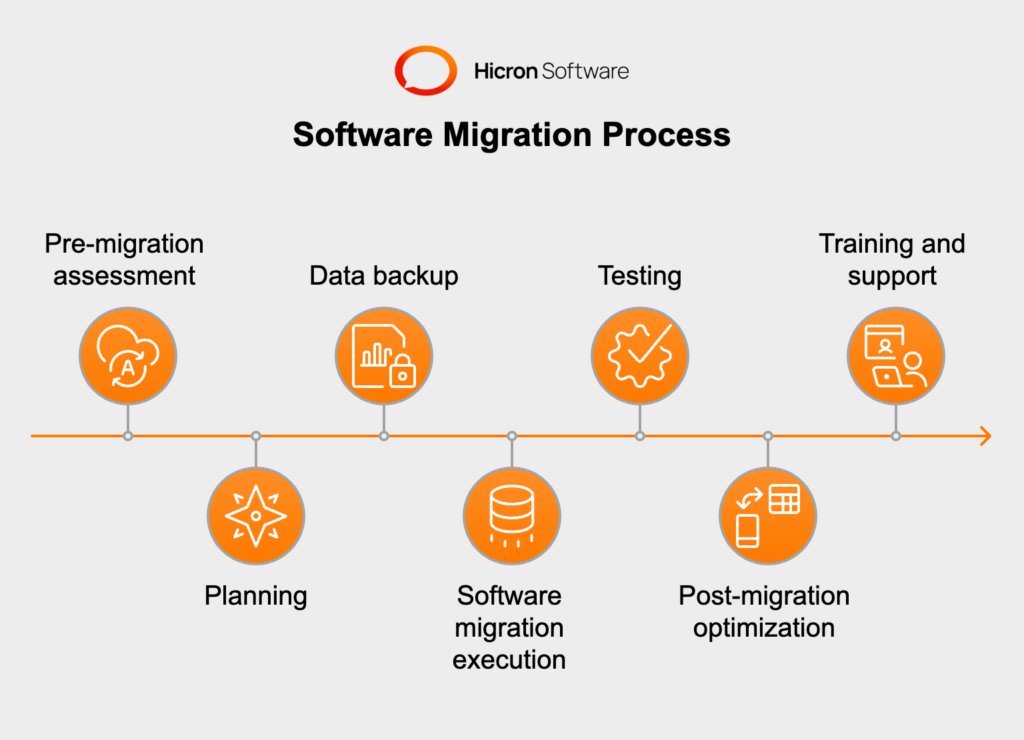
Let’s learn what the process of software migration looks like:
#1 Pre-migration assessment: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the existing system, analyzing its architecture, dependencies, and potential challenges to gain a deep understanding of its structure.
#2 Planning: Develop a robust software migration strategy that takes into account various factors such as data migration, potential risks, timeline, and resource requirements. This ensures a well-organized and efficient migration process.
#3 Data backup: Prioritize the backup of critical data and configurations to ensure the integrity and safety of information during the software migration. This step acts as a fail-safe mechanism in case any issues arise during the transfer.
#4 Software migration execution: Implement the selected software migration method carefully, ensuring a smooth transfer of both software and data to the target environment. This stage requires attention to detail to prevent any disruptions or loss of functionality.
#5 Testing: Perform rigorous testing of the migrated software to verify its functionality, performance, and compatibility with the new environment. Thorough testing helps identify any potential issues or bugs and allows for timely resolution.
#6 Post-migration optimization: Fine-tune the migrated application to optimize its performance in the new environment. Adjustments and optimizations are made based on the results of testing, ensuring the system operates at its optimal level.
#7 Training and support: Provide comprehensive training to end-users, enabling them to adapt to the migrated system smoothly. Additionally, offer ongoing support to address any issues or queries that may arise post-migration, ensuring a seamless transition for users.
Migrating an organization’s software is a significant endeavor that requires careful consideration. However, it also presents numerous advantages that can help the organization achieve its long-term goals. By preparing early and keeping an open mind, the benefits of software migration can be realized.

Let’s explore some of these advantages:
When it comes to software migration, there are several methods to consider, each tailored to different scenarios and requirements.
|
Strategy |
Description |
Benefits |
|
Lift-and-Shift |
Transfers software to a new environment with minimal changes. Quick and straightforward but may not fully utilize the target environment’s capabilities. |
Fast implementation, minimal disruption, and cost-effective for simple migrations. |
|
Replatforming |
Moves software to a different platform with slight modifications to optimize performance and compatibility, enhancing the use of the target environment. |
Improved performance, better compatibility, and partial optimization of the new environment. |
|
Refactoring |
Restructures the codebase to align with modern practices, improving scalability, maintainability, and security for long-term success in the new environment. |
Enhanced scalability, maintainability, security, and long-term adaptability. |
|
Complete Redesign |
Rebuilds legacy systems with modern technologies and frameworks, addressing technical debt and creating a future-proof, efficient software solution. |
Future-proof solution, access to modern features, and elimination of technical debt. |
Read about cloud migration strategies here.
#1 Lift-and-Shift: This method involves transferring the software application to a new environment with minimal changes. It offers a quick software migration process, but it may not fully leverage the potential of the target environment. While it provides a straightforward transition, organizations may miss out on optimizing their software for the new environment’s capabilities.
#2 Replatforming: With this approach, the software is moved to a different platform, often with slight modifications to optimize performance and compatibility. Replatforming allows organizations to make better use of the target environment’s capabilities. By fine-tuning the software, businesses can enhance its performance and ensure it aligns well with the new platform.
#3 Refactoring (Re-architecting): Refactoring is a powerful technique for enhancing software performance. By restructuring the codebase to align with modern architectural patterns and best practices, organizations can unlock improved scalability, maintainability, and security. This approach empowers businesses to fully harness the potential of their software, setting them up for long-term success in the new environment.
#4 Complete redesign: In cases where legacy systems have significant technical debt, a complete modernization may be necessary. This approach involves rebuilding the software using modern technologies and frameworks, enabling organizations to take advantage of the latest advancements in the industry. While more time-consuming and resource-intensive, a complete redesign can result in a highly efficient and future-proof software solution.
Selecting the best strategy for your software migration plan is important. In Hicron we have a methodical approach in order to help companies choose a software migration strategy that aligns with their unique requirements and business objectives. The structured software migration process consists of the following steps:
#1 Assessing and improving your current system
At our company, we take a thorough approach to assess your current system and identify areas for improvement. Our assessment includes evaluating the system’s architecture, functionality, performance, and dependencies. This comprehensive analysis provides us with a clear view of its strengths and weaknesses, allowing us to determine the necessary improvements and address any potential bottlenecks.
#2 Setting objectives for software migration process
In close collaboration with our clients, we define the goals for the software migration process. These objectives often include achieving enhanced performance, improved scalability, reduced maintenance costs, and the utilization of new features and technologies. By setting well-defined goals, we establish guiding principles that help us compare different software migration strategies effectively.
#3 Assessing risks of software migration
Our experienced engineers conduct a rigorous assessment of the potential risks and challenges associated with the transition. With this knowledge, we create mitigation plans that aim to minimize the potential effects of these risks. This proactive approach ensures a smoother and more successful software migration process.
#4 Analyzing technical requirements for the software migration process
We thoroughly analyze the technical requirements for your project. This includes considering the target architecture, platform compatibility, and integration potential. Additionally, we evaluate whether your current system aligns with the desired environment and determine if any adjustments are necessary for a seamless transition.
#5 Defining time and budget constraints
As part of our strategy selection process, we define the time frame within which the transition needs to be completed and the available budget. This step helps us narrow down our search and select a realistic and feasible strategy that meets the specific project requirements.
#6 Exploring software migration strategies
Together with our clients, we explore and discuss different software migration strategies based on their unique needs and goals.
#7 Selecting the best software migration strategy
Finally, we work with you to select the software migration strategy that best aligns with your organization’s objectives. We consider all the potential benefits and challenges associated with each strategy to make an informed decision. Our goal is to ensure a seamless and successful transition that meets your specific requirements.
|
Step |
Description |
|
Assess Current System |
Evaluate system architecture, performance, and dependencies to identify improvements. |
|
Set Migration Objectives |
Define goals like performance, scalability, and cost reduction with client collaboration. |
|
Assess Risks |
Identify potential challenges and create mitigation plans for a smoother transition. |
|
Analyze Technical Requirements |
Ensure compatibility with target architecture and desired environment. |
|
Define Time & Budget |
Establish timelines and budgets to guide strategy selection. |
|
Explore Strategies |
Discuss tailored migration strategies based on client needs. |
|
Select Best Strategy |
Choose the optimal strategy aligned with goals for a seamless transition. |
When it comes to choosing a software migration plan, partnering with a reputable company like Hicron Software can provide valuable expertise and guidance. Our experience in software development and legacy modernizations, combined with our focus on client needs and tailored solutions, makes us a reliable choice. By understanding your organization’s objectives, We can help you assess the risks, analyze technical requirements, and explore different strategies to ensure a smooth and successful transition.
The software migration process involves transferring software applications, systems, or data from one environment to another. This can include moving from an on-premise system to the cloud or upgrading to a newer version. Key steps include planning, discovery, data backup, testing, migration execution, and post-migration validation to ensure everything runs smoothly.
Program migration refers to the process of moving a software program from one platform, system, or environment to another. This could mean porting an application from one operating system to another, adapting software for cloud platforms, or transferring it to a different hardware infrastructure.
The four common types of data migration include:
Storage Migration: Moving data from one storage system to another.
Database Migration: Transferring data between different database formats or systems.
Application Migration: Moving data and related applications to a new computing environment.
Cloud Migration: Migrating data and systems from on-premise setups to cloud-based platforms.
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) migration involves moving a business function or application from on-premise software to a cloud-based platform. For example, migrating from an in-house CRM system to a SaaS solution like Salesforce. This migration often involves data transfer, user onboarding, and ensuring security compliance.
A common example is migrating from a legacy enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to a modern cloud-based ERP solution like Microsoft Dynamics or SAP S/4HANA. This involves transferring data, configuring software settings, and ensuring compatibility with existing business processes.
System migration typically follows these steps:
Assess Requirements: Identify the purpose and scope of the migration.
Create a Plan: Develop a detailed migration strategy, including timelines and resources.
Backup Data: Ensure all critical data is securely backed up.
Perform Testing: Test the migration process in a controlled environment to identify potential issues.
Execute Migration: Migrate the systems and monitor for errors.
Post-Migration Validation: Verify functionality, performance, and data accuracy in the new environment.
Migration in programming refers to making changes to a software system’s structure, codebase, or environment to support evolving requirements or updates. Examples include database schema changes, adapting code for new APIs, or transitioning to updated programming languages.
Technical migration involves updating or transferring the technical components of a system, such as migrating physical servers to virtual environments, transitioning to a new hardware platform, or modernizing outdated systems to align with new technologies. It focuses on enabling better performance, scalability, and efficiency.
