Why is a Mobile-first Approach Crucial for Real Estate Websites?
- July 14
- 10 min

Real estate websites are a goldmine for sensitive information, which is precisely why a security framework isn’t just a good idea—it’s a necessity. These platforms handle far more than just names and emails; we’re talking about sensitive personal and financial data like social security numbers, bank details, credit histories, and confidential legal documents. A single data breach could spell financial disaster for your clients, wreck your reputation, and land you in serious legal trouble with data protection laws. By setting up a formal security framework, you shift from simply reacting to problems to proactively preventing them. It’s about creating a solid, repeatable process to find risks, put controls in place, and prove you’re doing your due diligence. Ultimately, it builds the trust you need when clients hand over their most critical data for one of the biggest transactions of their lives.
Building a foundation for data protection starts with a simple mindset shift: treat client information like the critical business asset it is. This means protecting it with strong, layered security controls at every stage, from the moment you collect it to when you securely delete it. Your goal is to shield this data from anyone who shouldn’t see it, whether it’s being used by your team, sent across the internet, or just sitting in storage.
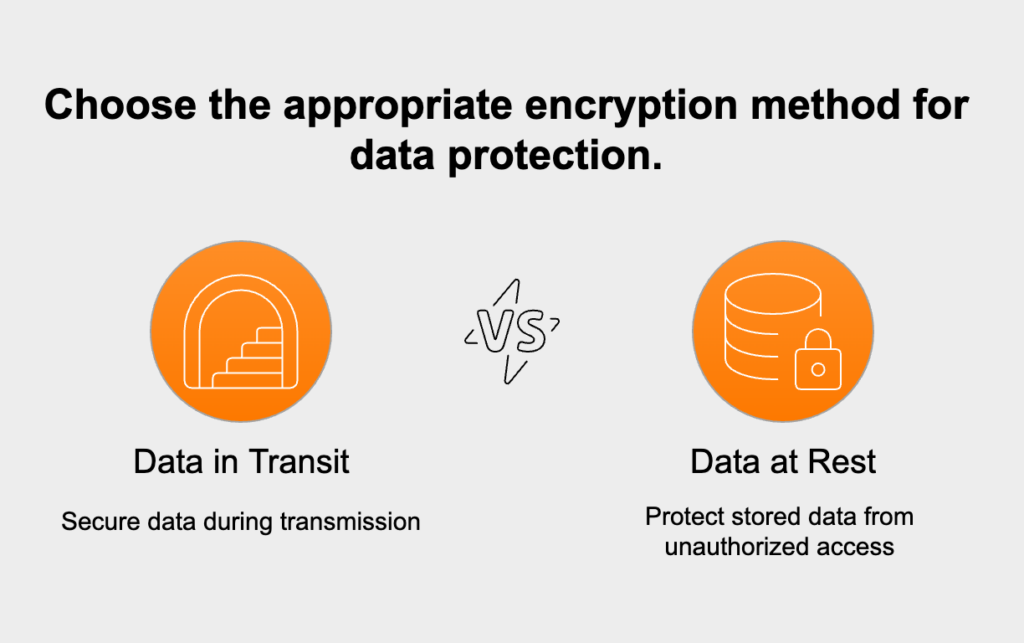
Think of encryption as your data’s last line of defense. If all else fails, encryption makes the information completely unreadable to anyone without the right key. It’s vital to apply it in two key scenarios:
Access to sensitive information must be governed by the principle of least privilege. In simple terms, employees should only be able to see the specific data they absolutely need to do their jobs. This is best done with a Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system, where permissions are tied to roles (like agent or admin) instead of individuals. It’s also vital to keep detailed access logs to see who accessed what and when. And don’t forget to have clear off-boarding procedures to immediately revoke an employee’s access the moment they leave the company.
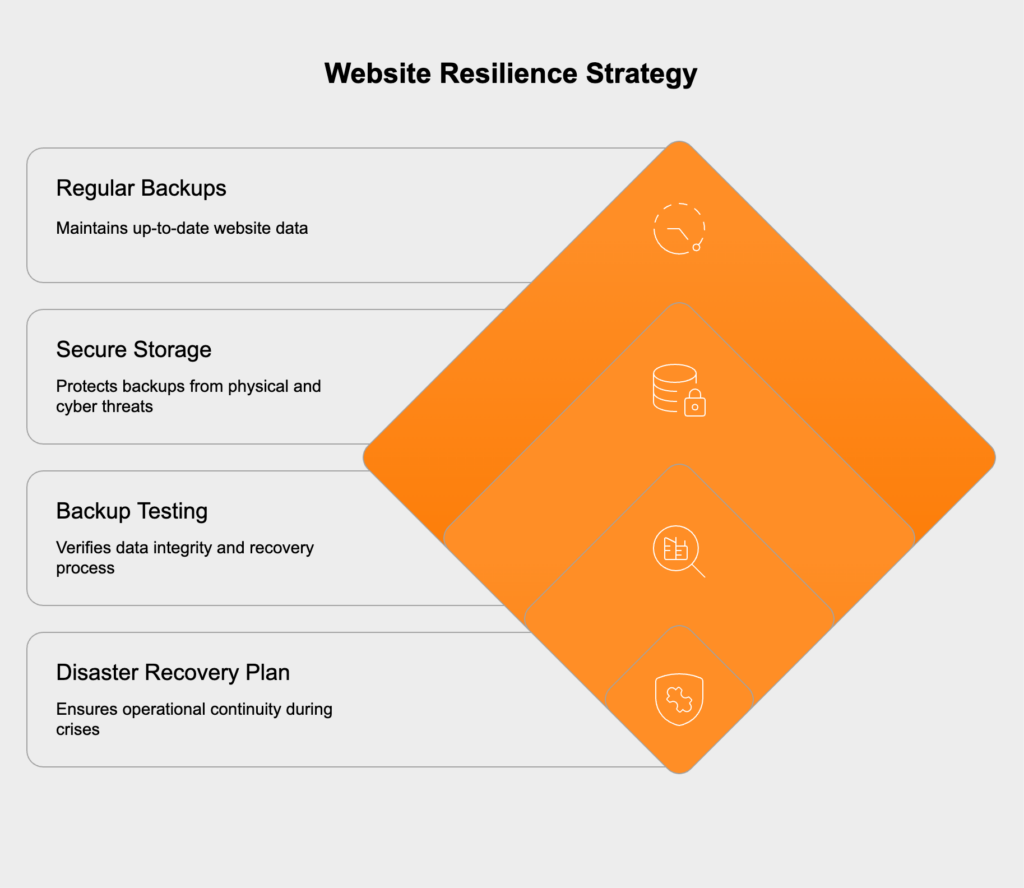
Effective backups and disaster recovery are all about resilience. Your entire website, including every file and the database, needs to be backed up automatically and regularly. These backups can’t just sit on the same server; they must be stored in a secure, geographically separate location to protect them from a fire, flood, or ransomware attack. Most importantly, you have to periodically test your disaster recovery plan. Restoring a backup is the only way to know for sure that the data is good and that your recovery process actually works when you need it most.
Staying compliant with data privacy laws means knowing your legal duties based on where you and your clients are located. It isn’t just a technical fix; it’s a business-wide process that requires transparency, good documentation, and a genuine respect for user rights. Following regulations like the EU’s GDPR or California’s CCPA is not optional. It also shows a commitment to handling data ethically, which is a major factor in building the trust of your clients.
A good privacy policy needs to be written in plain, easy-to-understand language and be easy to find on your website. It absolutely must include:

Navigating big regulations like GDPR and CCPA means taking specific steps. For GDPR, you need a lawful reason for processing data, must get clear consent when necessary, and be ready to handle data requests from users quickly. For CCPA, you have to provide a “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link if it applies to your business and tell users about their right to know what data you’ve gathered on them. For any real estate business, a great first step is to map out your data to see what you have, where it came from, and where it goes.
Vetting your vendors is absolutely critical because your security is only as strong as your weakest link. A data breach at your CRM provider, email marketing service, or cloud host can easily expose your client data—this is known as a supply chain risk. You have to perform due diligence on any vendor that touches your data. Check their security certifications, ask for compliance documents, and make sure your contracts hold them accountable for protecting the information you entrust to them.
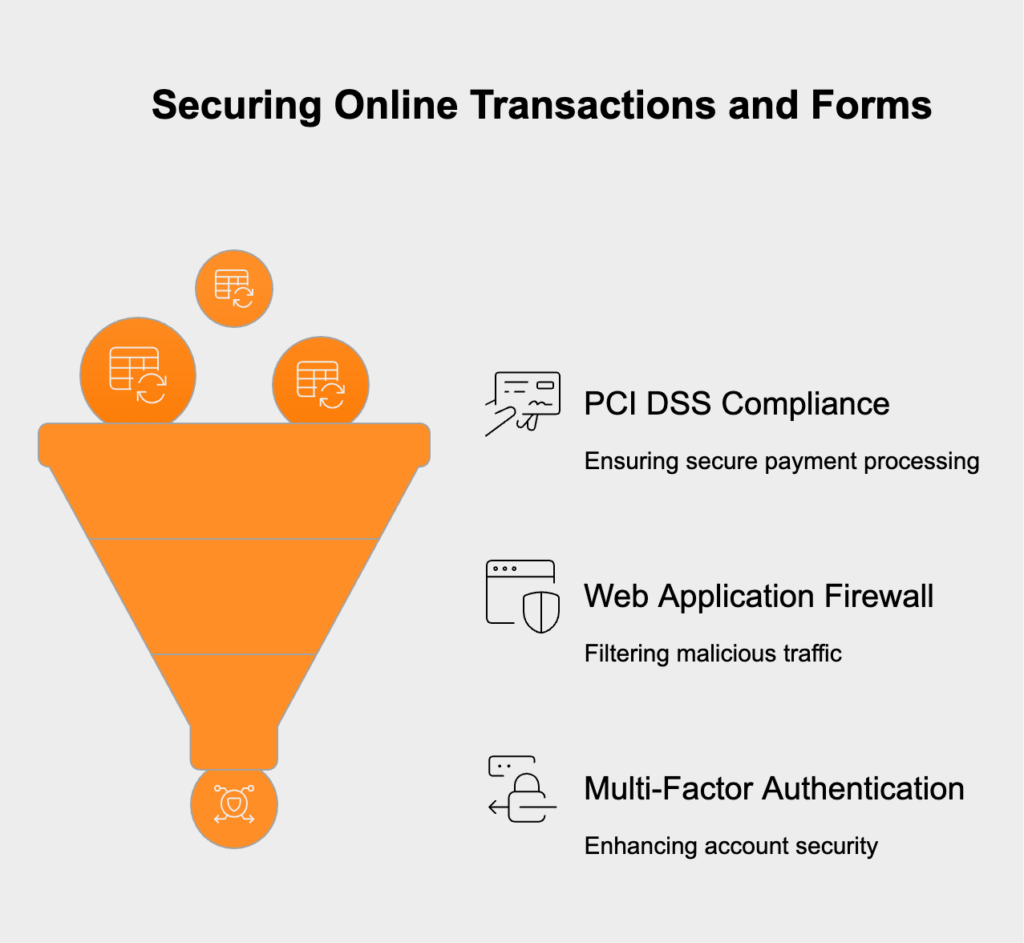
To properly secure online transactions and web forms, you need a few specific technologies working together to protect financial data and stop automated attacks. The first is handling payments correctly. While becoming fully PCI DSS compliant yourself is a massive undertaking, you can avoid most of the headache and risk by using a third-party, compliant payment processor. This keeps sensitive credit card details off your servers entirely. Next, a Web Application Firewall (WAF) is essential. It acts like a security guard for your website, filtering all incoming traffic to block common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting that are designed to steal data. Finally, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all admin and agent accounts. Requiring a second verification step—like a code sent to a phone—makes it dramatically harder for an attacker to get in, even if they’ve stolen a password.
Let’s be honest: people, both employees and clients, can make mistakes or be tricked into actions that compromise security. The best way to manage this human element is with a strategy that combines education with clear, actionable plans. It starts with your team. Regular, mandatory cybersecurity training is non-negotiable and should cover real-world threats like identifying phishing emails, using strong passwords, and securely handling client documents. You also need to educate your clients to protect themselves and limit your liability. A simple step is advising them to always verbally confirm wire transfer instructions to prevent fraud and warning them about phishing scams. Lastly, you absolutely need an incident response plan. This is a pre-written playbook for what to do when a breach happens. It ensures you can respond quickly and calmly to contain the threat, investigate what happened, and notify clients and regulators, which is often a legal requirement.
The technical backbone of your website’s security relies on your hosting environment and ongoing maintenance. When choosing a hosting provider, don’t just look at price. A secure host must provide a robust network firewall, regular malware scanning, and DDoS mitigation services. They should also support the latest software versions and have strong physical security at their data centers. But security isn’t a ‘set it and forget it’ task. You have to maintain it through continuous vigilance. This means running regular security audits and vulnerability scans to find weaknesses before attackers do. Continuously monitoring system logs helps you spot suspicious activity early, and using a structured approach like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework can help guide your ongoing security management.
Managing data from creation to deletion—and handling removal requests—is a huge part of modern data privacy. You need a clear, documented process for the entire data lifecycle. Laws like GDPR give clients the “right to erasure,” which means they can ask you to delete their personal information, and you have to be able to do it. This isn’t as simple as hitting a delete button. You must have a tested procedure to find every piece of a client’s data across all your systems, including backups, and then use secure methods to destroy it so it can never be recovered.
