How the Agency Model is Transforming the Automotive Industry
- January 09
- 12 min

The automotive industry’s traditional franchise model involves automakers selling vehicles to independent dealership franchises, which then handle the retail sales, customer service, and after-sales support. This model has long provided manufacturers with an extensive distribution network while allowing dealerships to profit from vehicle sales and services.
The automotive agency model represents a significant shift wherein automakers retain ownership of the inventory and sell directly to consumers, often through online platforms, while dealers facilitate test drives, deliveries, and some aspects of customer service.
Automakers are considering or transitioning to the agency model for several reasons. It allows for greater price transparency and consistency, eliminating the disparities caused by varying dealer markups. This model provides manufacturers with more direct control over the customer experience, enabling a more seamless and cohesive brand narrative. The agency model can streamline operations and reduce costs associated with maintaining large inventories at multiple dealership locations.
In an era defined by digital transformation and evolving consumer expectations, automakers see the agency model as a way to enhance customer engagement, leverage data more effectively, and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Early Vision and Implementation
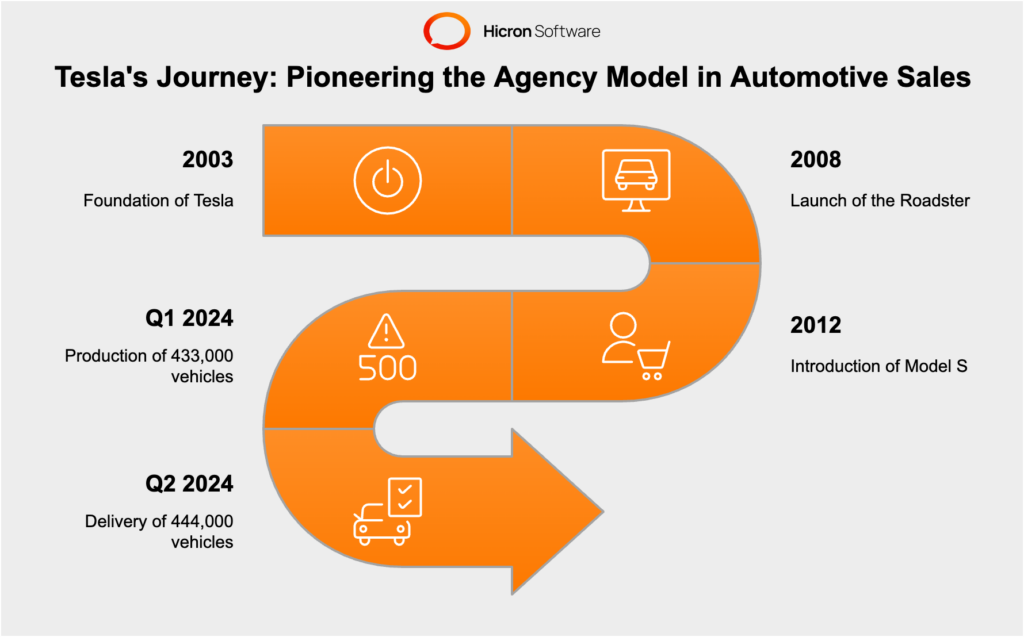
Foundation and Vision (2003-2008): Tesla, founded in 2003, aimed to sell directly to consumers, bypassing traditional dealerships.
Launch of Roadster (2008): Tesla promoted its first vehicle, the Roadster, through an online sales platform, allowing customers to customize and purchase their cars online.
Major Milestones
Model S Introduction (2012): The launch of the Model S solidified Tesla’s online sales strategy, offering detailed customization and purchase options directly on its website.
Expansion and Innovations: Tesla introduced features like virtual test drives, remote delivery, and over-the-air updates, enhancing the digital buying experience.
Challenges and Achievements
Legal Hurdles: Tesla faced legal challenges from established dealership networks but fought for the right to sell directly to consumers.
Market Acceptance: Consumers appreciated the convenience and transparency of Tesla’s direct-to-consumer model, influencing other automakers to consider similar approaches.
Tesla’s innovative online sales model has redefined customer expectations and demonstrated the benefits of a direct-to-consumer approach in the automotive industry.
Tesla, a pioneer in the agency model approach within the automotive industry, has demonstrated both growth and volatility in its sales figures in recent times. In the first quarter of 2024, Tesla produced over 433,000 vehicles but delivered approximately 387,000 vehicles. This represented a decrease of about 20.2% in quarterly deliveries compared to prior periods.
In the second quarter of 2024, Tesla’s production amounted to approximately 411,000 vehicles, with deliveries slightly higher at around 444,000 units. Despite challenges, including a decline in sales for the initial quarters of 2024, Tesla managed to sell more than 910,000 vehicles worldwide in the first half of the year, still outpacing competitors like China’s BYD.
These figures highlight the dynamic nature of Tesla’s sales performance, reflecting both its innovative market strategies and the challenges inherent in maintaining high growth rates.
Initial Goals for Online Sales by 2025
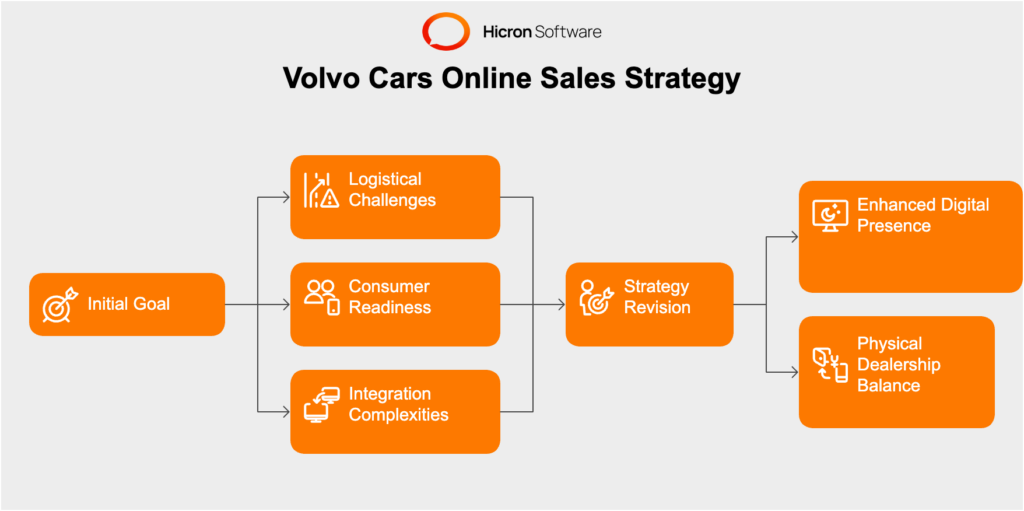
Volvo Cars initially set ambitious targets to complete half of its global vehicle transactions online by 2025. This goal was driven by a vision to leverage digital platforms for a more convenient and modern purchasing experience, aligning with the growing trend of e-commerce in various industries.
Factors Leading to the Revision of Targets
Despite the initial optimism, Volvo faced several hurdles that led to a revision of its targets. Key factors included logistical challenges, varying consumer readiness across different regions, and the complexities of integrating online sales with traditional dealership networks. As a result, Volvo adjusted its strategy to focus on enhancing its digital presence while maintaining a balance with physical dealerships.

Original Goals Set in 2018 and Subsequent Adjustments
In 2018 Mercedes-Benz announced that it aimed for 25 percent of its new and used vehicle sales to be completed online by 2022. This target was set as part of a broader strategy to embrace digital transformation and cater to tech-savvy consumers.
Insights from Market Responses and Strategic Changes
However, market responses and practical challenges necessitated a strategic shift. Mercedes-Benz extended the timeline to 2025 for “relevant new car sales,” acknowledging that widespread adoption of online sales would take longer than anticipated. Insights revealed that while many customers were open to online transactions, a significant portion still valued personal consultation and test drives, prompting Mercedes to refine its approach to blend digital convenience with traditional touchpoints.
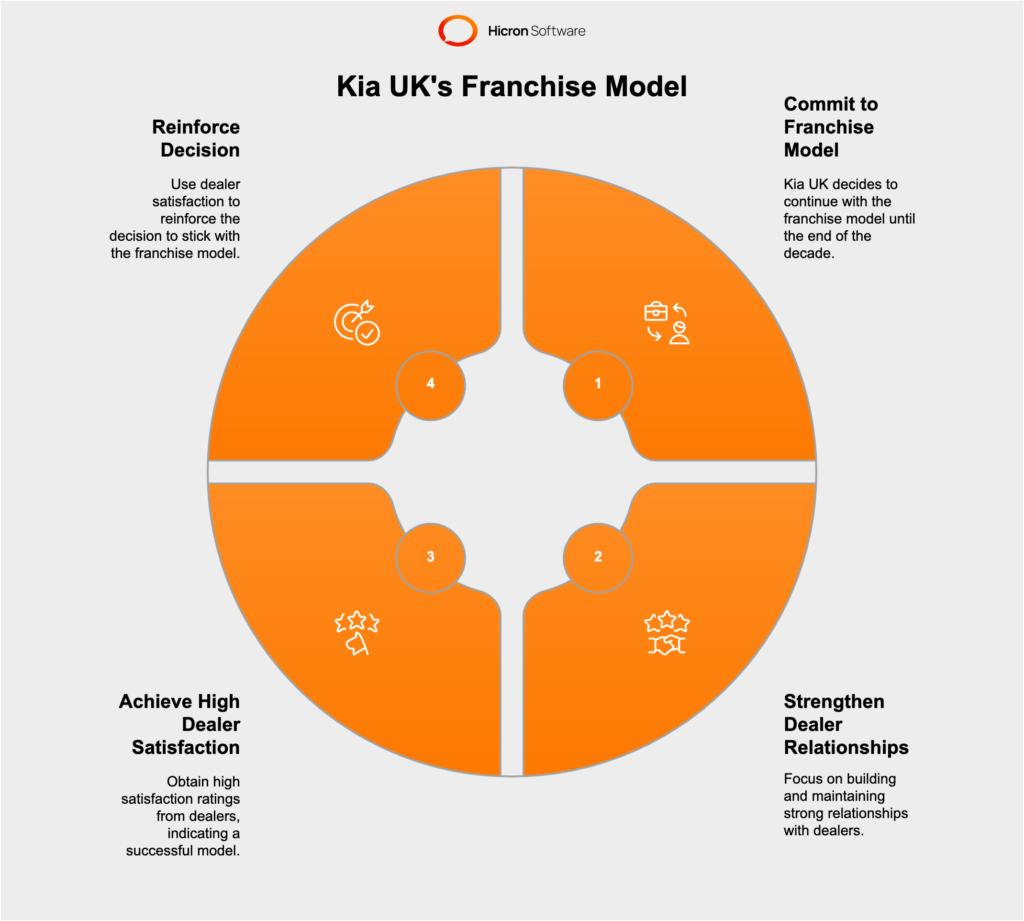
Decision to Stick with the Franchise Model Until the End of the Decade
Kia UK took a distinct approach by deciding to commit to the franchise dealer sales model for the rest of the decade. This decision was influenced by the strong relationships with their dealership network and the belief that the franchise model remains effective in delivering personalized customer service and building brand loyalty.
Key Takeaways from the NFDA Dealer Attitude Survey
The latest National Franchised Dealers Association (NFDA) Dealer Attitude Survey highlighted Kia UK’s successful dealer relations, with the brand achieving the highest overall rating of 9.5 out of 10. The survey, which saw 80 percent of Kia dealers respond, underscored the satisfaction and confidence of the dealer network in the existing sales model. This strong feedback reinforced Kia UK’s decision to maintain its current approach and continue supporting its franchise partners, ensuring consistent and high-quality customer experiences.
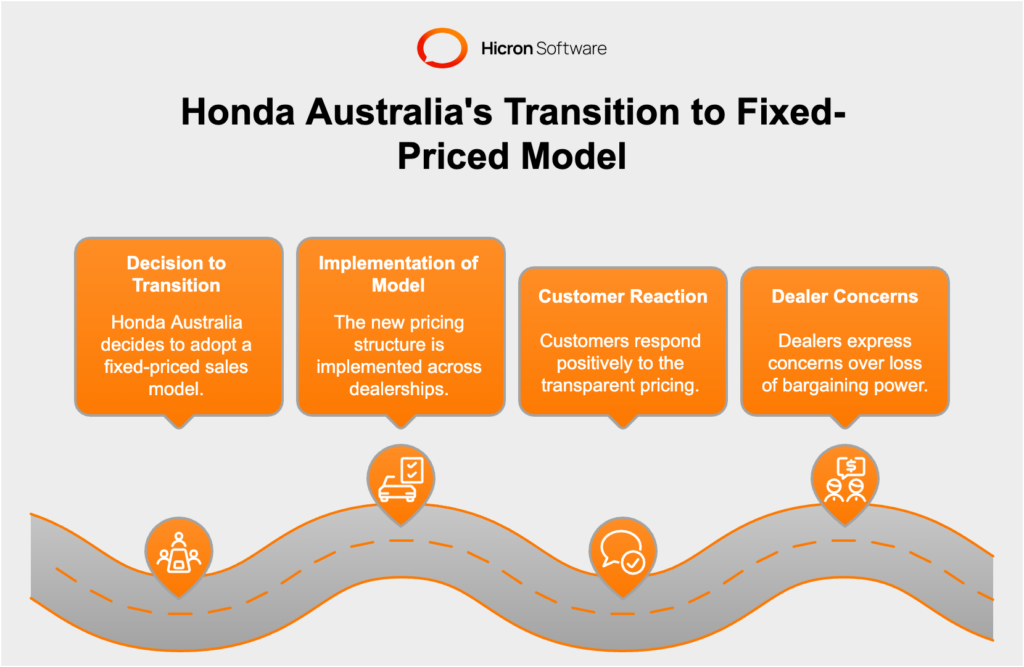
Overview of the Transition Process
Honda Australia made a bold move by transitioning to a fixed-priced sales model, eliminating traditional haggling and price negotiations in favor of a transparent pricing structure. This overhaul aimed to simplify the buying process and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring all customers paid the same price for the same vehicle, regardless of the dealership they visited.
Early Results and Market Feedback
Initial feedback from the market has been mixed. Many customers appreciated the straightforward pricing and the stress-free purchasing experience. However, some consumers and dealers expressed concerns over the loss of bargaining power and the potential impact on dealer profitability. This mixed reception highlights the complexities involved in moving away from traditional sales practices.
The outcomes of transitioning to the agency model in automotive sales vary widely, influenced by factors such as objectives, expectations, and the level of preparedness. This shift to fully online car sales is a complex and extended process for mature OEMs, marked by numerous challenges and lessons learned along the way. As such, these initiatives remain largely pilot projects intended to test the market. While current results may be mixed, the long-term strategy is clear: preparing for a future where potential buyers are increasingly familiar with digital interactions. By digitalizing sales now, automakers aim to align with evolving consumer preferences and ensure readiness for a more digitally-centric marketplace.
Flexibility in strategies based on market feedback has proven vital for automakers navigating the transition to new sales models. Successful adaptations often involve pivoting plans to better align with consumer and dealer expectations. For example, Mercedes-Benz extended its timeline for achieving online sales goals after recognizing the need for a more gradual shift, illustrating the importance of being responsive and agile in strategy formulation.
The importance of robust digital platforms for online transactions cannot be overstated. These platforms need to provide not only seamless and secure purchasing experiences but also user-friendly interfaces. Enhancing the customer experience with modern solutions, both with and without AI, is key. AI-driven tools can offer personalized recommendations and real-time assistance, while other technologies, such as virtual showrooms and detailed product configurators, can engage customers effectively even without AI. Tesla’s sophisticated online sales platform stands as a testament to the power of integrating cutting-edge technology in the automotive sector.
Successfully balancing the transition to an agency model with dealer interests is critical for maintaining a strong distribution network. Automakers must implement strategies to keep dealerships engaged and motivated, such as offering performance incentives, providing training on new digital tools, and maintaining open lines of communication about their evolving roles. Kia UK’s dedication to the franchise model, while gradually introducing digital enhancements, exemplifies how nurturing dealer relationships can support overall brand health and customer satisfaction.
Ensuring transparency and reliability in online sales is foundational to building consumer trust. Clear pricing policies, honest communication, and dependable customer support are essential components. Enhancing customer service through digital channels—such as offering live chat support, virtual consultations, and comprehensive online resources—can significantly bolster buyer confidence. For instance, Honda Australia’s fixed-priced model underscores the value of transparency and consistency in fostering trust among consumers during the purchasing process.
Many of these, hinge significantly on the strategic alignment and collaboration among the OEM, importer, and dealer. The above recommendations are only some of the strategies that can be applied and may be freely combined depending on larger strategies, budgets, and specified goals.
This is an initial examination based on publicly available information about the transition to the agency model in the automotive industry. It has uncovered significant insights and lessons. Flexibility in strategies based on market feedback, robust technological integration, maintaining strong dealer relationships, and fostering consumer trust are crucial elements for a successful shift. Case studies have shown that while some automakers have adapted to these changes, others continue to face challenges, highlighting the importance of a well-coordinated and adaptable approach.
The future of the agency model in the automotive sector remains a mixed bag of opportunities and uncertainties. On one hand, advancements in AI, machine learning, and augmented reality offer exciting possibilities for enhancing customer experiences and streamlining operations. Yet, the full impact of these technologies is still unfolding, and the industry’s ability to integrate them effectively remains to be seen. Emerging trends such as the development of comprehensive omni-channel strategies present potential pathways forward, but their widespread adoption and success are not guaranteed in such a distributed model. Automakers must prepare for a long haul filled with both potential benefits and unknowns.
