Innovation in Iteration: A Developer’s View on Quality & Legacy Code
- March 04
- 4 min

Large Language Models (LLMs) are designed to execute instructions effectively and are trained on massive amounts of data to understand the prompt and generate a response. As AI models become more competent, knowing how to frame your request matters as much as what you’re asking. Prompt engineering is designing high-quality prompts that guide LLMs to produce accurate outputs.
To maximize the benefits of AI tools, it’s essential to understand how these tools interpret user prompts. Furthermore, understanding the different types of prompts can help you effectively gather information from the AI. This article will explore effective prompting, including what it is, how it works, and tips for creating effective prompts.
AI prompts are the text instructions a user provides to an AI model to get the desired output. If you’ve used ChatGPT or Claude AI before, the text you typed in the chatbot is the prompt. AI prompts are crucial because they must be specific. More detailed and nuanced prompts deliver more relevant and helpful responses from generative AI tools. The key is crafting prompts that give the model a clear understanding of your desired output.

At a high level, these tools rely on natural language processing (NLP) to understand user requests. Crucially, they generate responses based on statistical probabilities of word sequences, making precise prompting essential for relevant outputs. When you feed a text prompt into a generative AI tool, the system first breaks your prompt into smaller bits – words or word fragments – that it can manage. The system uses its learned understanding of grammar, context, and wording to infer your intent and desired output. This intention recognition allows the AI to identify helpful patterns in the prompt. The system combines all these parameters to produce coherent content. The nuances of how a prompt is phrased can significantly impact the AI model’s interpretation and the resulting output, so it’s essential to frame your prompts precisely and clearly.
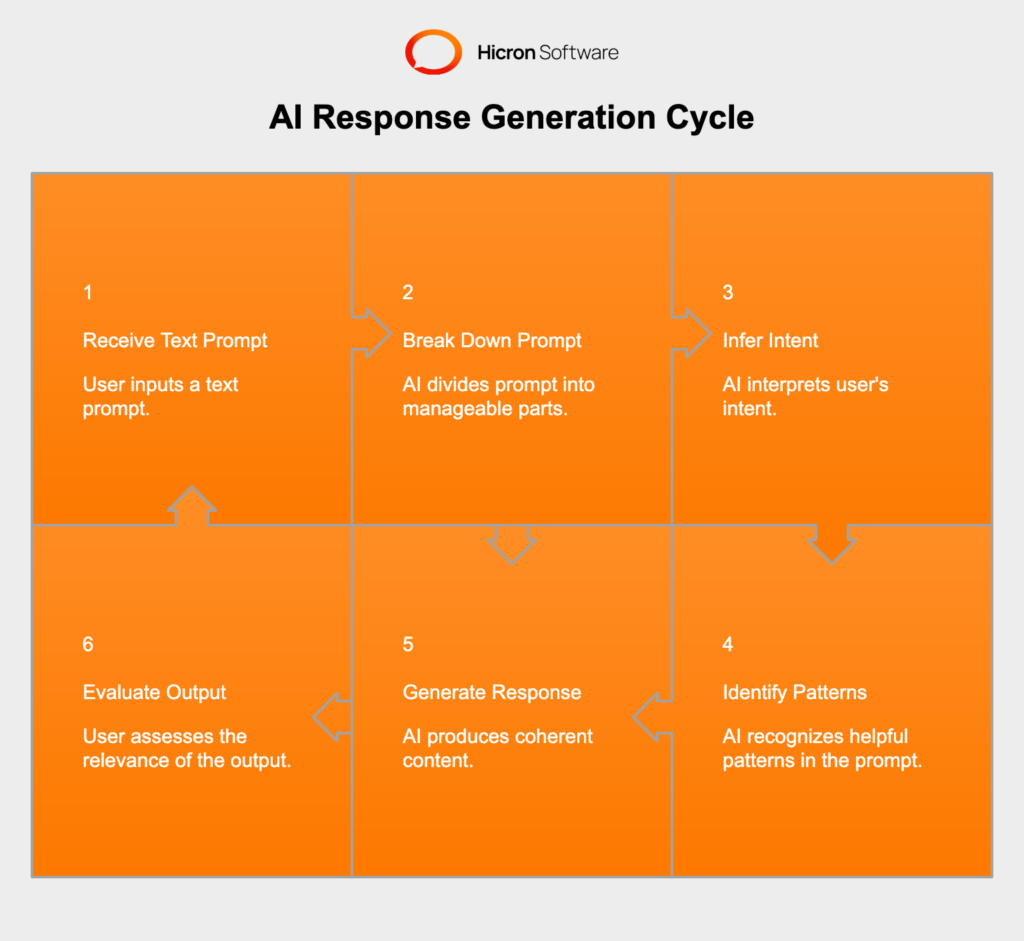
There are several different prompting techniques, including:
Example: “Translate the following text into French: ‘Hello, how are you?'”
|
Prompting Technique |
Description |
Example |
|
Zero-shot prompting |
The most straightforward technique in prompt engineering. It involves providing the model with direct instructions or questions, without giving sample answers or demonstrations. Instruct the model on what to do – no examples needed. |
“Translate the following text into French: ‘Hello, how are you?'” |
|
One-shot or few-shot prompting |
Provides the model with a handful of examples to mimic. This works well when your task requires structure, formatting, or nuance – things the model might struggle with. Show the model the pattern you want it to follow. |
“Convert the following text to JSON: Name: Alice, Age: 30 -> {“name”: “Alice”, “age”: 30}. Now convert: Name: Bob, Age: 25 ->” |
|
Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting |
Improves reasoning by explicitly asking the model to break problems into steps before reaching a final answer. Teach the model to think before it answers. |
“Explain how to set up a new email account. Break down the process into simple, numbered steps. Think step-by-step.” |
|
System prompting |
Shapes the model’s behavior by defining the overarching task and desired format. Define the task. Set the rules. Control the output. |
“You are a polite customer service bot. Your task is to answer questions about product returns. Always offer a solution. If you cannot answer, apologize and suggest contacting a human agent.” |
|
Role prompting |
Assigns the model a specific persona, such as a teacher, doctor, travel agent, or stand-up comedian. Give the model a personality and point of view. |
“Act as a seasoned software architect and provide three pros and three cons for migrating a legacy monolithic application to a microservices architecture.” |
Here are several tips that you can use to craft effective prompts:

Despite the significant benefits of effective prompting and AI integration, some crucial risks and challenges must be carefully considered. Being aware of these traps is essential for the responsible and effective use of AI tools.
Prompt injection is a technique used to hijack a language model’s output by injecting an untrusted command that overrides the original instructions of a prompt. This can easily occur if a user’s input is concatenated with a sensitive or system-level prompt without proper sanitization or separation. This allows harmful individuals to manipulate the model’s behavior, potentially leading to unintended or damaging outputs.
Prompt engineering is designing high-quality prompts that guide LLMs to produce accurate outputs. To get the most out of generative AI tools, it’s essential to know the types of prompts available and the strategies for optimizing every request. You can use these exciting and powerful technologies by writing prompts that complement an AI tool’s strengths.
Sources:
Prompt engineering is the process of designing high-quality prompts to guide AI models in generating accurate and relevant outputs. It’s important because well-crafted prompts improve the effectiveness and precision of AI responses.
Common techniques include zero-shot prompting, one-shot or few-shot prompting, chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting, system prompting, and role prompting, each tailored to specific use cases.
The phrasing of a prompt significantly impacts how an AI model interprets the request and generates responses. Clear, specific, and detailed prompts lead to more accurate and relevant outputs.
Risks include prompt injection (manipulating the model’s behavior), prompt leaking (exposing sensitive information), and jailbreaking (bypassing safety features to generate restricted content).
Tips include being clear and specific, providing examples, using positive instructions, experimenting with different formats, and iterating to refine the prompt for better results.
